E-Learning
Statistics
2023
E-Learning is no longer an unusual concept for most industries and educational institutions. As the pandemic situation evolved, so did the way we have been learning.

E-Learning is no longer an unusual concept for most industries and educational institutions. As the pandemic situation evolved, so did the way we have been learning.


While e-learning used to be a perk that only some institutions offered, it has now become the norm and a preference for the majority. Higher education e-learning platforms have supported students in completing their degrees at home while saving time and money.
Over the past few years, e-learning has grown tremendously. And more people than ever before can now pursue an education at their own speed, thanks to the internet. The data reported below reveals the details of the e-learning market and its projected future growth.


42% of companies who use e-learning generate more income.

In 2021, 27% of EU citizens aged 16 to 74 years reported participating in online courses.

Since 2020, 98% of universities have moved their classes online.

The global e-learning market is anticipated to climb nearly $1 trillion by 2028.

On average, E-Learning increases a learner’s retention rate to 82%.
In 2021, the e-learning market surpassed $315 billion. Massive open online courses (MOOCs) increased their reach from 300,000 to 220 million learners between 2011 and 2021. From 2012 to 2019, the number of hybrid students at traditional universities went up by 36%, with the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 accelerating that growth by an additional 92%. These figures are not surprising given the rapid growth of e-learning in recent years.
Global statistics concerning e-learning show a rise in the industry. Moreover, different studies report that adopting an online educational platform enables a better balance between work and study, while others don’t necessarily agree with this point.
The data presented below show what parts of the world were the most affected by e-learning and which countries show a remarkable projected future growth.
To begin with, StuDocu analyzed Google Trends for e-learning searches. As expected, the searches for this keyword spiked during the pandemic period. However, what’s worth noting is that even during the post-pandemic period (July 2022), the trend is still higher than before the pandemic started.
During the pandemic, social interactions were reduced; thus, the safest way out was to use online courses, which provide a secure substitute for education and training.
Data from Europe shows that in 2021, 27% of EU citizens aged 16 to 74 years reported having taken an online course or using online learning material, a rise from 23% in 2020.
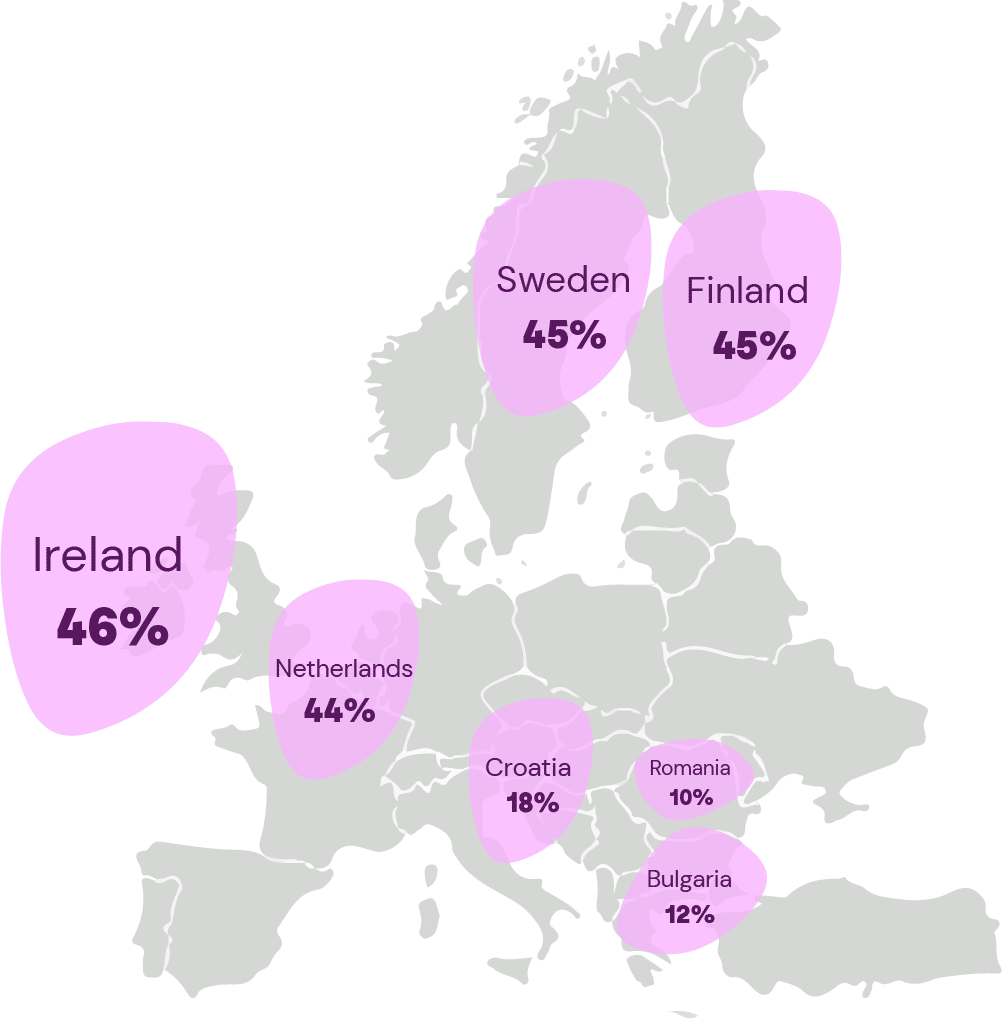
Ireland had the largest percentage (46%) of citizens ages 16 to 74 enrolled in online courses or accessing online learning resources in 2021. Finland and Sweden came in second with a registered share of 45%, followed by the Netherlands with 44%.
On the low end of the scale, Croatia (18%), Bulgaria (12%), and Romania (10%) were among the countries with the lowest percentages of people taking online courses or using online learning resources.
When it comes to course distribution by subject, the highest percentage of course distribution is in the fields of Business and Technology, with 20.9% and 20.2% respectively.
Other fields like Social Sciences, Science, Humanities, and Education & Training have a comparatively lower percentage of course distribution, with 11.2%, 9.5%, 9%, and 7.4% respectively.
Following the COVID-19 pandemic, the Asia e-learning market established a positive correlation strongly supported by four major factors: technology, government initiatives, blended learning, and penetration rate.
The closing of colleges, schools, and other learning institutions during the COVID-19 pandemic created numerous opportunities for e-learning, increasing its popularity among the general public.
According to Allied Market Research, the Asia e-learning market was valued at $38.25 billion in 2020 and is expected to reach $162.15 billion by 2030, with a 15.7% CAGR from 2021 to 2030.
Given how much workers value learning and development opportunities, it should be no surprise that organizations that support their employees’ ongoing education have higher retention rates.
Corporate e-learning is here to stay. Employee training will increasingly take place online as more businesses move remote. Between 2020 and 2024, the US e-learning market is anticipated to grow by $12.81 billion. Globally, the corporate e-learning market is predicted to grow by $37.8 billion from 2020 to 2025, at a compound yearly growth rate of 13%.
E-learning plays a huge role in learners’ retention rate as well. After analyzing a dozen of case studies with thousands of participants, we found that on average, e-learning increases a learner’s retention rate to 82%.

Compared to traditional learning, corporate e-learning requires 40% to 60% less time to complete.

On average, E-Learning increases a learner's retention rate to 82%.

77% of businesses used e-learning in some capacity in 2017.

So far, 90% of US corporations have incorporated online learning.

42% of companies that use e-learning generate more income.
In the fall of 2020, approximately 75% of undergraduate students were enrolled in at least one distance education course, and 44% (7.0 million) of all undergraduate students took distance education courses exclusively.
Students enrolled in at least one distance education course at the undergraduate level increased by 97% in 2020 compared to the previous fall prior to the pandemic (11.8 million vs. 6.0 million). The number of undergraduate students enrolled solely in distance education courses increased by 186% in 2020 compared to 2019 (7.0 million vs. 2.4 million).
In the fall of 2020, around 8.6 million college students in the United States were enrolled solely in online education courses offered by postsecondary institutions.

Approximately half of Dutch, German, and US students believe COVID-19, social isolation, and long-distance schooling have positively impacted their university’s digitalization.
Students from the Netherlands and Germany saw significant improvements in their educational institutions’ digital transformation processes. Although students in all three countries surveyed believe their teachers’ or professors’ digital skills could improve, most students believe their educators do not need to upgrade their skills.
Although one-third of the Dutch and US students and an additional 53% of German students spent the lockdown studying exclusively online, they have doubts whether a fully online academic experience would suit them the best.
Data also shows that, of the Dutch students, 3 out of 4 are more easily distracted during online classes, compared to about half of German and US students.
Similarly, nearly 75% of Dutch students struggle to stay focused, compared to 49% and 56% of German and US students, respectively. As a result, more than 60% of German and half of Dutch students reported that the pandemic had a negative impact on their overall academic performance.
To address the focus and concentration issues and improve results, 6 out of 10 students from all three countries would prefer, when possible, a hybrid form of education that combines online and physical classes.
The benefits of e-learning, including the positive impact on climate change, have proven to be very important.
According to a study by Ohio University on their electricity consumption over five years, the amount of energy used in one university might range from 120 million kWh to 126 million kWh. Data on the benefits of e-learning shows that moving classes online will cut energy consumption by 90%. Moreover, if a twenty-student course is moved online, it could save 1,200 tons of CO2 emissions and eliminate more than $1 million in travel expenses.
Traditional face-to-face learning requires students to travel from various regions, which has a significant environmental impact. It is estimated that nearly 60% of students take a car to school, which results in heightened pollution and emission levels. Faculty and staff who do not commute to campus on a daily basis and instead commute on a less frequent schedule save energy and pollution.
A study by the University of West Georgia found that online learning contributes to cutting CO2 emissions by 5-10 tons per semester for every hundred students.
Digital documents are a major component of online education. Assignments and textbooks are submitted electronically. The National Wildlife Federation states that 60% of school waste comes from paper. A typical school uses around 2,000 sheets per day! That is about one tree per week. But when using digital texts and other digital resources instead of paper handouts helps reduce the carbon footprint and paper waste.
Online learning is also helpful in reducing food and plastic waste by minimizing the use of cafeterias. In the US, schools reportedly waste 530,000 tons of food annually. Another advantage of online learning is that it may reduce the need for disposable lunch items like plastic bags and water bottles, even when students still eat at home.
In a few words, online learning helps by:
There is a lot of hope for the future of online education. The e-learning market had a value of just about $315 Billion in 2021. The global e-learning market will reach approximately $1 trillion by 2028, with a rise of 20% CAGR during the forecast period of 2022-2028, in addition to the current value of $315 billion.
The global e-learning market is projected to grow by $200 billion by 2026.
The European e-learning market is projected to grow by $28.36 billion by 2024.
The U.S. e-learning market is projected to grow by $21.64 billion by 2024.
Fortunately, learning is no longer restricted to old-fashioned techniques; most of it now can take place online. And that’s what makes e-learning undoubtedly to be considered the future.
That e-learning has become more accessible thanks to data visualization and task and time management tools is another factor that demonstrates that the sector will flourish in the future.

