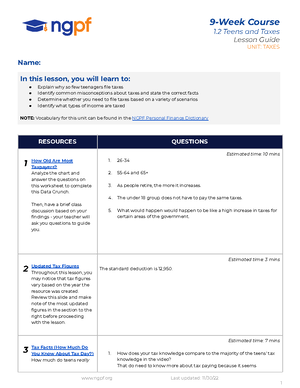
- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Rosal Lubana - U4L3: Waves Gizmo
Subject: History Revolutions
57 Documents
Students shared 57 documents in this course
Level • Grade:
Secondary School
• 10Was this document helpful?

U4L3 : Waves Gizmo
Link: Student Exploration: Waves
Directions: Follow the instructions to go through the simulation. Respond to the questions and
prompts in the orange boxes.
Vocabulary: amplitude, compression, crest, frequency, linear mass density, longitudinal wave, medium, period,
power, rarefaction, transverse wave, trough, wave, wavelength, wave speed
Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
1. A buoy is anchored to the ocean floor. A large wave approaches the buoy. How
will the buoy move as the wave goes by?
The buoy will move up and down because the wave will push it.
2. The two images show side views of ocean waves. How are the two sets of waves different?
The two images showing the two different sides
of the ocean are different because the first image
of the wave is higher than the second image of
the ocean wave.
Gizmo Warm-up
Ocean swells are an example of waves. In the Waves Gizmo, you will observe
wave motion on a model of a spring. The hand can move the spring up and
down or back and forth.
To begin, check that the Type of wave is Transverse, Amplitude is 20.0 cm, Frequency is 0.75 Hz, Tension
is 3.0 N, and Density is 1.0 kg/m. (Note: In this Gizmo, “density” refers to the linear mass density, or mass
per unit length. It is measured in units of kilograms per meter.)
1. Click Play ( ). How would you describe the motion of a transverse wave? Click Pause ( ). Notice the
crests (high points) and troughs (low points) of the wave.
A transverse wave moves from left to right, but the particles inside move up and down. The
waves move left to right while the hand moves up and down.
2. Click Reset ( ). Choose the Longitudinal wave and increase the Amplitude to 20.0 cm. Click Play.
How would you describe the motion of a longitudinal wave? Click Pause. Notice the compressions in
the wave where the coils of the spring model are close together and the rarefactions where the coils are
spread apart.
In this wave, the hand is moving from the left to the right as well as the wave.
Have Mrs. Graham come check your work BEFORE you move on
Reproduction for educational use only. Public sharing or posting prohibited. © 2020 ExploreLearning™ All rights reserved