- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Pitocin-oxytocin - ATI active learning template
Course: nursing care of women and families (NUR 4450)
21 Documents
Students shared 21 documents in this course
University: Madonna University US
Was this document helpful?

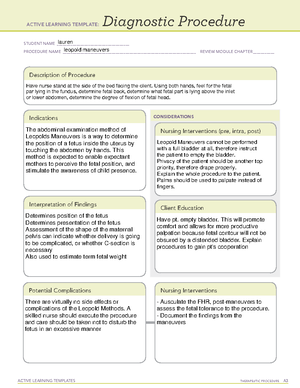
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES THERAPEUTIC PROCEDURE A7
Medication
STUDENT NAME _____________________________________
MEDICATION __________________________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER ___________
CATEGORY CL ASS ______________________________________________________________________
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE:
PURPOSE OF MEDICATION
Expected Pharmacological Action
Complications
Contraindications/Precautions
Interactions
Medication Administration
Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness
Therapeutic Use
Nursing Interventions
Client Education
lauren
pitocin/oxytocin
stimulates smooth muscle of uterus and
mammary glands
Never give drug simultaneously
by more than one route, Don’t
give bolus injection; use infusion
pump. Give by piggyback
infusion so that it may be
stopped without interrupting IV
line.
Carboprost tromethamine, Cyclopropane anesthetics,
Dinoprostone, Drugs that prolong QT interval, Misoprostol,
Vasoconstrictors
Contraindicated: when vaginal delivery isn’t advised, in fetal distress when
delivery isn’t imminent, prematurity/other obstetric emergencies, patients with
severe toxemia or hypertonic uterine patterns
Caution: patients with invasive cervical cancer/previous cervical or uterine
surgery (including cesarean section), grand multiparity, uterine sepsis,
traumatic delivery, or overdistended uterus.
subarachnoid hemorrhage, seizures, coma, arrhythmias, abruptio placentae,
hemorrhage, anaphylaxis, death from oxytocin-induced water intoxication, uterine
rupture, afibrinogenemia. HTN, PVCs, nausea, vomiting, tetanic uterine contractions,
impaired uterine blood flow, pelvic hematoma, increased uterine motility.
Fetal: brain damage, seizures, low Apgar scores at 5 minutes, death, bradycardia,
arrhythmias, PVCs, retinal hemorrhage, jaundice
induce labor, reduce postpartum bleeding,
abortion
Patients on oxytocin must be under observation.
Discontinue oxytocin infusion immediately if uterine
hyperactivity or fetal distress occurs. Administer oxygen to
mother. Use for induced labor only when pelvis is known
to be adequate, vaginal delivery is indicated, fetal maturity
is assured, and fetal position is favorable. Use drug only in
hospital where critical care facilities and prescriber are
immediately available. Monitor intake and output.
Antidiuretic effect may lead to fluid overload, seizures, and
coma from water intoxication. Monitor and record uterine
contractions, HR, BP, intrauterine pressure, fetal HR, and
character of blood loss at least every 15 minutes.
client gives birth/client shows no sign of postpartum
hemorrhage, fetus is aborted (if given for this reason)
Explain use and administration of
drug to patient and family.
Instruct patient to promptly report
adverse reactions (site irritation,
nausea, bleeding, blurred vision,
difficulty speaking, wheezing,
itching, swelling).