- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
ATI learning template metoprolol clinical
Course: Medical-Surgical Nursing Clinical Lab (NUR1211L)
69 Documents
Students shared 69 documents in this course
University: Miami Dade College
Was this document helpful?

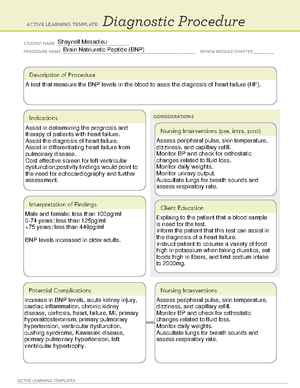
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES
Medication
STUDENT NAME _____________________________________
MEDICATION __________________________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER ___________
CATEGORY CL ASS ______________________________________________________________________
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE:
PURPOSE OF MEDICATION
Expected Pharmacological Action
Complications
Contraindications/Precautions
Interactions
Medication Administration
Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness
Therapeutic Use
Nursing Interventions
Client Education
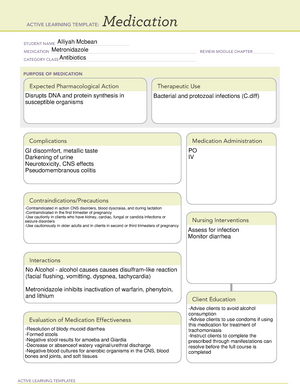
Shaynell Mesadieu
Metoprolol
antiangial antihypertensive
Block stimulation of Beta1 andrenergic
receptors.
This drug can be taken orally
and Intravenously.
General anesthesia, phenytoin and verapamil may cause myocardial depression.d
digoxi, verapmil,diltiazem or clonidine increase risk of bradycardia.
Antihypertensives, alcohol, nitrates increase risk of hypotension.
Concurrent use of amphetamines, cocaine, ephedrine, epinephrine, norepinephrine,
phenylephrine, or pseudoephedrine may result in excessive hypertension or
bradycardia.
Thyroid medication may decrease effectivness.
Contraindicated in: Uncompensated HF, pulmonary edema,
cardiogenic shock, bradycardia, heart block or sick sinus syndrome.
Use cautiously: Renal impairment, hepatic impairment, sensitivity to
beta blockers, pulmonary disease, DM, Thyrotoxicosis, patients with a
history of severe allergic reactions.
fatigue, weakness, anxiety, depression, dizziness, drowsiness,
insomnia, memory loss, mental status changes, nervousness,
nightmare, bradycardia, HF, pulmonary edema, hypotension, rash,
blurred vision, stuffy nose, hypergylcemia, hypoglycemia,
constipation, diarrhea, etc.
Decrease BP and heart.
Decreased frequency of attacks of angina pectoris.
Decreased rate of cardiovascular mortality and
hospitalization in patients with heart attack.
Monitor BP, ECG, and pulse frequently
during dose adjustment and
periodically during therapy.
Monitor vital signs and ECG every 15
minutes.
Monitor intake and output.
Asess routinely for signs of HF.
Decrease in BP.
Reduction in frequency of anginal attacks.
Prevention of MI.
Instruct to take drug as directed. Never
skip or double dose.
Teach patient and family how to monitor
BP biweekly and pulse daily.
Caution patient to avoid driving.
Advise patient to change position slowly to
minimize orthostatic hypotension.
Caution patient that this drug may increase
sensitivity to cold.