- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Cardiovascular Exemplars 08232020
Course: Professional Nursing III (NUR 2790)
59 Documents
Students shared 59 documents in this course
University: Rasmussen University
Was this document helpful?

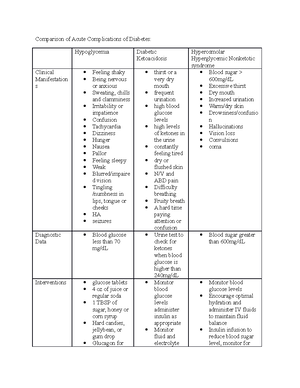
Comparison of Cardiovascular Exemplars:
Angina Acute Myocardial Infarction
Pathophysiology Temporary imbalance between
coronary artery’s ability to supply
oxygen and cardiac muscle’s demand
for oxygen. Ischemia limited in
duration and does not cause
permanent damage to myocardial
tissue. Stable and unstable.
Starts with unstable angina. There is reduced blood flow in a
coronary artery, often d/t rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, but
the artery is not completely occluded. As the cells are deprived of O2,
ischemia develops, cellular injury occurs, and lack of O2 leads to
infarction or death of the cells.
Etiology Physical exertion, exposure to cold,
eating a heavy meal, stress
The sudden constriction or narrowing of the coronary artery
The decrease in O2 supply occurs from acute blood loss,
anemia, or low BP
A rapid HR, thyrotoxicosis, or ingestion of cocaine causes an
increase in the demand for O2
Assessment
Findings
(including
Diagnostics)
Patients present with ST changes on
12-lead ECG but will not have
changes in troponin or CK levels.
Cardiac Stress Test
Nuclear Stress test
Dizziness
Fatigue
Nausea
SOB
Sweating
S/S
Chest pain
SOB
Indigestion
Tachycardia / tachypnea
Coolness in extremities, perspiration, anxiety and restlessness
Fever
ECG; CPK-MB; LDH; Troponins; myoglobin; electrolytes; CXR;
Coronary angiography
MRI
Exercise stress test
Nursing Diagnosis Decrease Cardiac Output
Acute Pain
Ineffective cardiac tissue perfusion
Decreased Cardiac output
Acute pain
Interventions
(including meds
Meds
Nitrates; ASA; anticoagulants; beta
Morphine for pain
Ace Inhibitors; beta blockers