- Information
- AI Chat
ATI-Prototype-Drugs
Professional Nursing 3 (NU278/NUR2790)
Rasmussen University
Recommended for you
Preview text
MODULE 2: NEUROLOGICAL SYSTEM (PART 1)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM DEPRESSANTS
DRUG THERAPY FOR SLEEP DISORDERS
■■ Benzodiazepine – temazepam (Restoril) ■■ Non-benzodiazepine – zolpidem (Ambien)
DRUG THERAPY FOR MUSCLE SPASMS
■■ Centrally acting muscle relaxants – baclofen (Lioresal) ■■ Peripherally acting muscle relaxants – dantrolene (Dantrium) Photosentivity
DRUG THERAPY FOR SEIZURE DISORDERS
■■ Hydantoins – phenytoin (Dilantin)-> skin rash (Steven Johnson syndrome). If oral Hydroxyzine spension-> u should sake well ■■ Iminostilbenes – carbamazepine (Tegretol) ■■ Valproic acid – valproic acid (Depakote, Depacon, Depakene)
DRUG THERAPY THAT SUPPORTS ANESTHESIA
■■ Local anesthesia – lidocaine (Xylocaine) ■■ General anesthesia/barbiturates – sodium thiopental (Pentothal) ■■ General anesthesia/benzodiazepine – midazolam (Versed) ■■ General anesthesia/opioid – fentanyl (Sublimaze) Nabulphine: miosis, constipation, urinary urgency
DRUG THERAPY FOR ADHD AND NARCOLEPSY
■■ Amphetamines – amphetamine and dextroamphetamine sulfate (Adderall) ■■ Methylphenidate – methylphenidate (Ritalin, Concerta) ■■ Non-amphetamine – modafinil (Provigil)
DRUG THERAPY FOR PARKINSON’S DISEASE
■■ Dopamine-replacement drugs – levodopa/carbidopa (Sinemet) ■■ Direct-acting dopamine receptor agonists – pramipexole (Mirapex) ■■ Indirect-acting dopamine receptor agonists/MAOs – selegiline (Eldepryl, Zelapar ODT)
DRUG THERAPY FOR ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE
Cholinesterase inhibitors – donepezil (Aricept, Aricept ODT) NMDA receptor antagonist – memantine (Namenda)
DRUG THAT TREAT MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS ■■ Immunomodulators – Interferon beta-1a (Avonex, Rebif), Interferon beta 1b (Betaseron)
DRUG THAT TREAT MIGRAINE HEADACHES ■■ Serotonin agonists – sumatriptan (Imitrex) Transdermal: take as needed,, activate 15 min
PSYCHOTHERAPEUTIC DRUGS
DRUG THERAPY FOR ANXIETY DISORDERS
■■ Benzodiazepines – diazepam (Valium), alprazolam (Xanax)-> monitor paradoxical effect: insomnia and excitation, hypotension, inability to reacall events (amnesia) ■■ Non-benzodiazepines – buspirone
DRUG THERAPY FOR DEPRESSION ■■ Tricyclic antidepressants – amitriptyline- block reutake of nore and serotonin-> risk for orthostatic hypotension, avoid alcohol, should take at bedtime due to drowsiness and sedation ■■ SSRIs – fluoxetine (Prozac) ■■ SNRIs – venlafaxine ■■ MAOIs – phenelzine (Nardil) ■■ Atypical antidepressants – bupropion HCL (Wellbutrin)
DRUG THERAPY FOR BIPOLAR DISORDER
■■ Lithium (0.8-1) – lithium carbonate (Lithobid)-> engage in strenuous exercise, t ake 7-10 day to achieve, therapeutic dose 300 SA: muscle weakness Toxic: hypokalemia: dehydration, diarrhea, sweating, excessive exercise in hot weather, diuretic use, low sodium diet) ■■ Antiepileptic drugs (AED) – valproic acid (Depakote) Paroxetine (antidepressant)- SSRI Valproate, Carbamazepine (anticonvulsants), smooth stabilizer
DRUG THERAPY FOR SCHIZOPHRENIA
■■ Conventional antipsychotics – chlorpromazine, fluphenazine sleepiness should subside within a week Anticholinergic effects Haloperidol EPS Tardive dyspnea: tongue thrusting and lip smacking, facial grimacing and eye blinking Dystonia: repetitive muscular contraction cause twisting of the body Clozapine Agranulocytosis ■■ Atypical antipsychotics – risperidone (Risperdal)
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM DRUGS
Drug therapy for glaucoma ■■ Beta adrenergic blocker – betaxolol (Betoptic), timolol (Timoptic) ■■ Cholinergic agonists – pilocarpine (Isopto Carpine) regular schedule for rest of life ■■ Cholinesterase inhibitors – echothiophate (Phospholine Iodide) Prostaglandin, latanoprost DRUG FOR RETINAL DETACHMENT: Phenylephrine (mydriatic meds) dilate pupil after surgeries
MODULE 3: MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
■■ Nonopioid – dextromethorphan suppress urge to cough Expectorants – guaifenesin (Mucinex)
Stimulant secretions to improve cough products
Mucolytics – acetylcysteine- unsual odor
MODULE 5: THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
DRUG THERAPY FOR HYPERTENSION
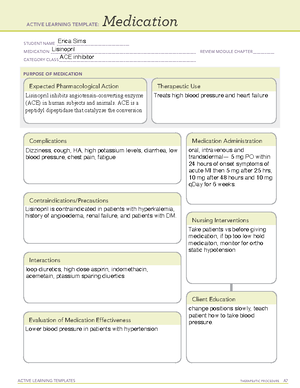
RAAS Suppressants ■■ ACE inhibitors – captopril (Capoten) ■■ ARBs – losartan (Cozaar) ■■ Aldosterone antagonists – eplerenone (Inspra) ■■ Direct renin inhibitors – aliskiren (Tekturna) Calcium channel blockers – nifedipine (Adalat, Procardia) Sympatholytics ■■ Alpha 1 adrenergic blockers – doxazosin (Cardura) ■■ Beta adrenergic blockers – atenolol (Tenormin), metoprolol (Lopressor) ■■ Adrenergic neuron blockers – reserpine ■■ Centrally acting alpha 2 agonists – clonidine (Catapres) ■■ Alpha/beta blockers – carvedilol (Coreg) Direct acting vasodilators – hydralazine
DRUG THERAPY FOR HEART FAILURE Diuretics ■■ Thiazide diuretics – hydrochlorothiazide (HydroDIURIL) ■■ Loop diuretics – furosemide (Lasix) High ceiling loop diuretic Bumetanide ■■ Potassium-sparing diuretics – spironolactone (Aldactone) Cardiac glycosides – digoxin (Lanoxin) Sympathomimetics – dobutamine Phosphodiesterase inhibitors – milrinone (Primacor)
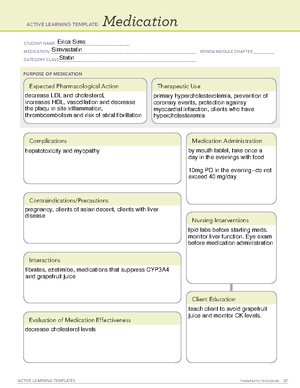
DRUG THERAPY FOR CORONARY HEART DISEASE Antilipemic ■■ HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) – atorvastatin (Lipitor) ■■ Fibrates – gemfibrozil (Lopid) Antianginals ■■ Nitrates – nitroglycerin (Nitrostat, Nitro-Dur), isosorbide (Isordil)
Headade is SA-> use analsgesic
DRUG THERAPY FOR CARDIAC DYSRHYTHMIAS Class I/sodium channel blockers ■■ Class IA – quinidine, procainamide
■■ Class IB – lidocaine (Xylocaine) ■■ Class IC – flecainide (Tambocor) Class II/beta adrenergic blockers – propranolol (Inderal) Class III/potassium channel blockers – amiodarone (Cordarone) Class IV/calcium channel blockers – verapamil (Calan)
MODULE 6: THE HEMATOLOGIC SYSTEM
DRUG THERAPY FOR ANEMIA
Iron deficiency anemia – iron freparations – ferrous sulfate (Feosol) taking between meal to increase absorption , iron dextran (INFeD) Pernicious anemia – vitamin B 12 , cyanocobalamin (Nascobal, Cyanoject) Megaloblastic (macrocytic) anemia – folic acid
DRUG THERAPY FOR BLEEDING DISORDERS
Hemophilia ■■ Factor VIII – plasma-derived (Hemofil-M) or recombinant factor VIII (Advate) ■■ Factor IX – plasma-derived (AlphaNine SD) or recombinant factor IX (BeneFix) ■■ Desmopressin – desmopressin (DDAVP, Stimate)
DRUG THERAPY TO PREVENT AND DISSOLVE THROMBI Anticoagulants ■■ Factor Xa and thrombin inhibitor – heparin- not dissolve clots, stop new clots from forming, work immediately ■■ Factor Xa inhibitor – enoxaparin (Lovenox) ■■ Vitamin K inhibitor – warfarin (Coumadin), interact with ginkgo biloba (suppress coagulant Antiplatelets ■■ Salicylics – aspirin (Ecotrin) ■■ ADP Inhibitors – clopidogrel (Plavix) Thrombolytics – alteplase (Activase)
DRUG THERAPY THE SUPPORTS HEMATOPOIESIS Erythropoietic growth factor – epoetin alpha (Epogen, Procrit) Leukopoietic growth factor – filgrastim (Neupogen) Thrombopoietic growth factors – oprelvekin (Neumega)
MODULE 7: THE GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
DRUG THERAPY FOR PEPTIC ULCERS
Histamine 2 -receptor antagonists – ranitidine hydrochloride (Zantac) Take a night to prevent nocturnal acid. Proton pump inhibitors – omeprazole (Prilosec) Mucosal protectant – sucralfate (Carafate), require no water Antacids – aluminum hydroxide (Amphojel) Prostaglandin E analog – misoprostol (Cytotec) Antibiotics – amoxicillin (Amoxil), metronidazole (Flagyl), tetracycline
Synthetic prostaglandin – dinoprostone (Cervidil) Ripen cervix Drug therapy to accelerate fetal lung maturity Betamethasone (Celestone) Drug therapy to prevent and treat seizures Magnesium sulfate-> the nurse should now that the women is 1st (respiratory) and then FHR
Drug therapy that stops uterine contractions Beta 2 -adrenergic agonists – terbutaline (Brethine): weakened urine, increase FHR,
hyperglycemia, tremor, nervousness, headade. LIFE THREATENING: dyspnea
Male reproductive drugs Testosterone hormone Drug therapy for replacement of androgens Testosterone – testosterone (Androderm, Delatestryl) Drug therapy for benign prostatic hypertrophy and outflow disorders 5-alpha reductase inhibitor – finasteride (Propecia, Proscar) Alpha-adrenergic receptor antagonists – tamsulosin (Flomax) Drug therapy for erectile dysfunction PDE5 inhibitor – sildenafil (Viagra) Urinary tract drugs Drug therapy for urinary incontinence/over-active bladder Anticholinergics – oxybutynin chloride (Ditropan) Drug therapy for urinary retention Cholinergics – bethanechol (Urecholine)
MODULE 9: THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
DRUG THERAPY FOR DIABETES MELLITUS
Oral hypoglycemics ■■ Sulfonylureas – glipizine (Glucotrol) ■■ Meglitinides – repaglinide (Prandin) ■■ Biguanides – metformin (Glucophage) ■■ Thiazolidinediones – pioglitazone (Actos) ■■ Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors – acarbose (Precose) ■■ Gliptins – sitagliptin (Januvia) Injectable hypoglycemics ■■ Insulin – lispro (Humalog), Regular (Humulin R), insulin glargine (Lantus) NPH (Humulin N) peaks 6-14hr-> eat snake after 8hr to prevent hypoglycemia then recheck in 15 mins ■■ Amylin mimetics – pramlintide (Symlin) ■■ Incretin mimetics – exenatide (Byetta) Hyperglycemics – glucagon (GlucaGen)
DRUG THERAPY FOR THYROID DISORDERS
Thyroid replacements – levothyroxine (Synthroid) Expected: decrease in TSH-> Increase in T4, improve mood Antithyroid drugs ■■ Propylthiouracil – propylthiouracil (PTU)-> agranulocytosis ■■ Radioactive iodine – iodine-131 ( 131 I, Iodotope)
DRUG THERAPY FOR HYPOTHALAMIC DISORDERS
Growth hormone – somatropin (Genotropin, Nutropin, Humatrope, Serostim) Antidiuretic hormone – desmopressin (DDAVP, Stimate, Minirin )
DRUG THERAPY FOR ADRENAL DISORDERS
Glucocorticoids – hydrocortisone (Solu-Cortef) Mineralocorticoids – fludrocortisone (Florinef)
MODULE 10: THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
DRUG THERAPY TO PREVENT DISEASE
Childhood vaccines Adult and older adult vaccines
DRUG THERAPY FOR CANCER
Cytotoxic drugs Antimetabolites ☐☐ Folic acid analog – methotrexate ☐☐ Pyrimidine analog – cytarabine (Cytosar-U, DepoCyt) ☐☐ Purine analogs – mercaptopurine (Purinethol) Alkylating agents ☐☐ Nitrogen mustards – cyclophosphamide ☐☐ Nitrosoureas – carmustine (BiCNU) Platinum compounds – cisplatin Antitumor antibiotics ☐☐ Anthracyclines – doxorubicin (Adriamycin, Doxil)
Antimitotics ☐☐ Vinca alkaloid – vincristine ☐☐ Taxanes – paclitaxel (Taxol, Abraxane) Topoisomerase inhibitors – topotecan (Hycamtin) Hormonal agents ■■ Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists – leuprolide (Lupron, Lupron Depot) ■■ Androgen receptor blockers – flutamide ■■ Estrogen receptor blockers – tamoxifen (Soltamox) ■■ Aromatase inhibitors – anastrozole (Arimidex) ■■ Monoclonal antibody – trastuzumab (Herceptin) Biologic response modifiers ■■ Interferon – interferon alfa-2a (Roferon-A), interferon alfa-2b (Intron A) Targeted antineoplastic drugs ■■ BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor – imatinib (Gleevec)
DRUG THERAPY FOR URINARY TRACT AND OTHER BACTERIAL INFECTIONS
Drugs that inhibit folic acid synthesis ■■ Sulfonamides – trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Septra) ■■ Urinary tract antiseptics – nitrofurantoin (Macrodantin)
DRUG THERAPY FOR TUBERCULOSIS
Antimicobacterials – isoniazid (INH, Nydrazid-IM form), rifampin (Rifadin)
DRUG THERAPY FOR PARASITIC INFECTIONS
Antiparasitics – metronidazole (Flagyl), chloroquine (Aralen)
DRUG THERAPY FOR FUNGAL INFECTIONS Antifungals ■■ Polyene antibiotics – amphotericin B (Fungizone) ■■ Azoles – ketoconazole
DRUG THERAPY FOR VIRAL INFECTIONS
Antivirals – acyclovir (Zovirax)
DRUG THERAPY FOR GOUT
Colchicine. SA: diarrhea (toxicity), anorexia, muscle pain Phencyclidine (angel dust) intoxication: hypertension, tachy, seizures, coma-> ad vasodialtors (nitroprusside), hyperthermia
Cyclobenzaprine to relieve muscle spasm that cause pain of fractures
Pain scale: FLACC (2-7months) Oucher (3-13 years) FACES (3 years) Visual Analog Scale
Metered dose inhaler: Sake 3-5 s, wait 20-30s between inhalations
Colesevepam for low density lipoprotein level-> take this meds 4hr after other meds
Inhlation Anthrax: Cipro, doxycycline, amoxicillin
Fat overload: elevated temp-> multiple organ damage
Behavior indicate pain: restlessness, grimacing, moaning, clenching
Take out subclavian venous cath-> use Valsalva maneuver by holding breath and bearing down-> prevent air from entering lumen, hear, and pulmonary circulation, flat position or Trendelenburg
IM injection: inject to deltoid if 0-1ml, 2in below acrmonion process, 23 -25 gauze IV: dorsal metacarpal vein
Other: cephalic, basilica Cause pain-> meet the nerve ends-> remove and reinsert IV fluid volume excess: crackles upon auscultation-> dyspnea Infiltration: edema at injection site, damp dressing Phlebitis: erythema, throbbing pain, warmth, streak formation Venipuncture: antecubital fossa (forearm)
Cath policy: clean perineal twice daily, ONLY IRRIGATE IF OBSTRUCTION, CHANGE IF BLOCKAGE-> check for kinks or twisting to prevent infection Spina bifida: catherize every 4hr Change in length = dislodgment, catheter occlusion = diff administer fluids
NG: 15-30ml water after each medication, prior administration, after givng multiple medications
HERBS:
Echianeca boots immunue system, treat fever-> reduce meds treat TB Ginger treat vertigo and motion sickness Ginkgo biloba increase ability to walk futher sistance Saw palmetto blocks testosterone receptors, relieve urinary frequency Black cohos relieve menopausal symptoms: hot flashes Feverfew prevent migraine, increase risk for bleeding due to suppress platelet Valerian promotes sleep Milk thistle reduces effectiveness of oral contraceptives Ephedra elevate BP Comfrey wound healing Licorice treat GI problems Chamomile calming agents Garlic lower cholesterol Isofamide, antineoplastic stop cancer-> renal failure Vincristine, antineoplastic-> paresthesia and paralysis Daunorubin antitumor-> cause edema and dyspnea, cardiomyopathy
ATI-Prototype-Drugs
Course: Professional Nursing 3 (NU278/NUR2790)
University: Rasmussen University

- Discover more from: