- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Med Term Ch 15 - Chapter 15!! - MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
Course: Medical Terminology (HSC 236)
39 Documents
Students shared 39 documents in this course
University: The University of Tampa
Was this document helpful?

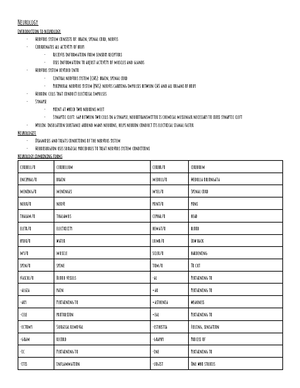
Chapter 15: endocrinology
Introduction to endocrinology
- Endocrine system consists of group of glands: two adrenal glands, two ovaries (or two testes), four parathyroid glands, the pancreas, the pineal gland, the
pituitary gland, thymus gland, and thyroid gland
- Plays vital role in homeostasis: maintaining a stable internal environment, glands secrete hormones: internal chemical messengers, travel through
bloodstream to target organs, and regulate activity level of target organ
- Subspecialty of internal medicine, endocrinology diagnose and treat conditions that develop as a result of hormone imbalance, hypersecretion: too much
hormone, hyposecretion: too little hormone
Endocrinology combining forms
aden/o
Gland
adren/o
Adrenal glands
adrenal/o
Adrenal glands
crin/o
To secrete
glyc/o
sugar
glycos/o
sugar
oophor/o
ovary
orchi/o
testes
ovari/o
ovary
pancreat/o
pancreas
parathyroid/o
Parathyroid gland
pineal/o
Pineal gland
pituitar/o
Pituitary gland
testicul/o
testes
thym/o
Thymus gland
thyr/o
Thyroid gland
thyroid/o
Thyroid gland
acr/o
extremities
carcin/o
cancer
cyt/o
cell
ophthalm/o
eye
toxic/o
poison
-al
Pertaining to
-an
Pertaining to
-ar
Pertaining to
-centesis
Puncture to withdraw fluid
-cyte
cell
-dipsia
thirst
-ectomy
Surgical removal
-edema
swelling
-emia
Blood condition
-ic
Pertaining to
-ism
State of, condition
-itis
inflammation
-logist
One who studies
-logy
Study of
-malacia
Abnormal softening
-megaly
enlarged
-oid
resembling
-oma
Tumor, mass
-osis
Abnormal condition
-otomy
Cutting into
-pathy
disease
-pexy
Surgical fixation
Students also viewed
- 1. Basic Chart - Piaget Theory of Cognitive Development I
- Med Term Ch 11 - chapter 11! - MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
- Med Term Exam 4 - exam 4 review! - MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
- Med Term Ch 2 - chapter 2!! - MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
- Med Term Exam 1 - review for exam 1 - MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
- Med Term Ch 4 + 3 - chapter 3 and 4 quiz review - MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
Related documents
- Med Term Ch 12 - chapter 12!! - MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
- Med Term Ch 14 - Chapter 14!! - MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
- Med Term Ch 6 - Chapter 6!! - MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
- Med Term Ch 13 - Chapter 13!!! - MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
- Med Term CH 16 - Chapter 16!! - MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
- Med Term Ch 17 - Chapter 17!! - Medical Terminology