- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Accelerated Motion Worksheet Answers
Course: General Physics (PHYS 1120)
22 Documents
Students shared 22 documents in this course
University: University of Nebraska at Omaha
Was this document helpful?

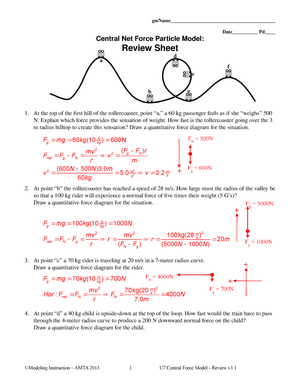
Name
Date Pd
Uniformly Accelerated Particle Model Worksheet 4:
Interpreting Graphs of Accelerated Motion
Object A:
a. Where on the graph above is the object moving most slowly? How do you know?
The object is not moving at locations B and F. We know this because the slope of the tangent
is zero (in other words the curve is horizontal at those points). If the student interprets the
question to mean where is it actually moving but at the slowest rate, the locations would be just
before and after B and F. Reasoning is that the slope is very small.
b. Between which points is the object speeding up? How do you know?
The object is speeding up between B and C and also between F and G. We know this because
between those points the slope is continually increasing in steepness.
c. Between which points is the object slowing down? How do you know?
The object is slowing down between A and B and also between E and F. (and also after G) We
know this because between those points the slope is continually decreasing in steepness.
d. Where on the graph above is the object changing direction? How do you know?
The object is changing direction at B and F. We know this because the slope is going from
negative to positive or positive to negative at these points.
©Modeling Instruction - AMTA 2013 1 U3 Uniform acceleration - ws 4 v3.0
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
positon
tme