- Information
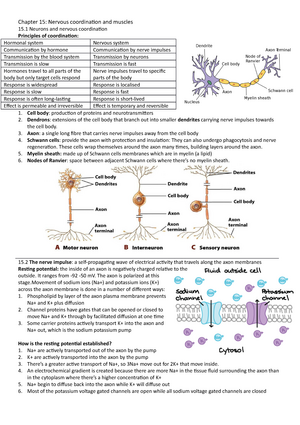
- AI Chat
This is a Premium Document. Some documents on Studocu are Premium. Upgrade to Premium to unlock it.
Was this document helpful?
This is a Premium Document. Some documents on Studocu are Premium. Upgrade to Premium to unlock it.
Costs and benefits of economic growth essay
Subject: Economics
623 Documents
Students shared 623 documents in this course
Degree • Grade:
Sixth Form (A Levels)
• A2 - A LevelWas this document helpful?

‘Discuss the costs and the benefits of economic growth’ (25)
Essay Plan:
Introduction:
-definition of economic growth:
long-term expansion of the productive potential of the economy
increase in the value of national output/national expenditure.
-why is it important
major objective of policy for most governments
enables the increase of living standards, the improvement of tax revenues and
creates more job opportunities
measures the growth of the economy’s overall well-being
Paragraph 1: Benefit
-Point: Economic growth leads to an improvement of living standards that can be measured
by real GNI per capita and quality of life
-Definitions: living standard
generally, the quality of housing, material comfort, and wealth experienced by an
individual or group
-Evidence:
The average worker in the United States would have had to work for 333 hours to buy a
fridge in 1894, now, a better fridge can be bought in 20% of that time by an average worker.
Life expectancy of a person born in Japan in 1880 was 35 years, the life expectancy in Japan
has gone up to 83.84 years in 2017.
-Explanation:
Causes:
Increase in AD +AS
As average incomes rise and there are more goods and services available for consumption,
more people will be able to afford the goods and services, thus resulting in an improvement
of living standards.
Consequences:
•improved resources for education
•more spending on healthcare
•increased tax revenue
•enables more consumption
Students also viewed
Related documents
- Monopoly 25 Marker
- Evaluate the extent to which a reduction in taxation will increase a country’s rate of economic growth 20 marks
- Assess the view that regulation is a better policy for dealing with the problem of air pollution than the allocation of property rights or taxation
- Assess the view that as the rate of economic growth increases, a rise in inflation is inevitable.
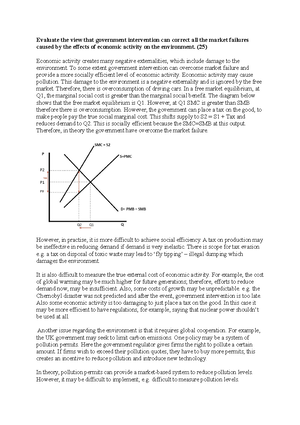
- Evaluate the view that government intervention can correct all the market failures caused by the effects of economic activity on the environment
- To what extent does the cost of globalisation outweigh benefits