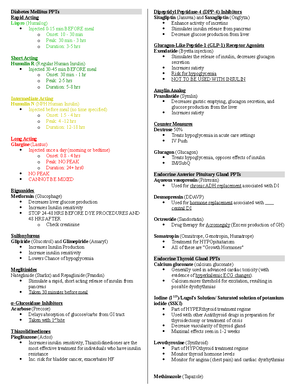
- Information
- AI Chat
Psych Final Exam Notes
Mental Health Nursing (NUR 3328)
Baylor University
Preview text
Psych Final Exam Notes
Personality disorders
Cluster A
Paranoid – suspicious, hold grudges, unforgiving, very critical but difficulty accepting criticism, cold, unemotional, no sense of humor Intervention: avoid being overly friendly, be neutral, clear and straight forward, get it in writing
Schizoid – social isolation, no desire for relationships, parallelism, emotional coldness, flat affect Intervention: don’t try to re-socialize, don’t be overly friendly, need thorough assessment questioning
Schizotypal – withdrawn and aloof, odd beliefs, fantasy, magical thinking, social anxiety, limited close relationships, precursor to schizophrenia. Intervention: respect need for isolation, and same as cluster A
Cluster B
Antisocial – ignore social rules, manipulative, exploitative, dishonest, lack remorse for actions, involved in criminal activity. CAN BE CHARMING b/c manipulative. Substance abuse # highest rate. Usually use projection or splitting as defense mechanism Intervention: avoid flattery,seductiveness,guilt. Set clear expectation for all staff, writing!
Borderline – intense/unstable relationship. IMPULSIVE. Act out instead of expressing emotions, suicidal, self-mutilating in response to rejection, emotional emptiness is chronic, splitting (all or nothing)
Intervention: avoid rejecting or rescuing pt, be straightforward, be physically present, avoid manipulation. !!! they provoke most extreme countertransference!!!
Narcissistic – fragile self-esteem, use others to meet needs, entitlement, belittle others, lack empathy, controlling, power struggle, overcompensation for low self-esteem
Intervention: convey confidence, avoid power struggle,
Histrionic – Draw attention to themselves, concerned with appearance, excessive emotionally, emotionally shift from person to person, shallow, no empathy, instant gratification with affection
Cluster C
Dependent PD – overly agreeable, passive, unable to be w/o relationship, clingly, difficulty with decisions. Intervention: identify real vs perceived needs.
OCD – inflexible, rigid, need to be in control, perfectionist, work emphasized, decreased decisions, highly moral/ethical, Intervention: avoid power struggle, look for intellectualization, rational, reaction formations
Avoidant – social inhibition, social phobia, feeling inadequate, fears criticism/rejection, feel inferior and unappealing, avoid new situations
Intervention: be friendly, reassuring, gradually introduce social situations
Mood Disorders: In assessment, change is seen.
Bereavement and loss can be seen in maladaptive response to depression
- Depression higher in women
- Culture affects expression, presentation, and treatment of depression
Factors: Loss of interest or pleasure, impaired social/occupational functioning for 2 weeks, no history of manic behavior, symptoms not related to substance/medical condition,
Criteria: depressed mood, anhedonia, weight loss or gain, insomnia/hypersomnia, psychomotor agitation/retardation, fatigue or loss of energy, feelings of worthlessness, inappropriate guilt, decreased concentration, decreased decision making, recurrent thoughts of death
Intervention: SAFETY FIRST! Then physiological balance, indentifying factors/stressors.
- offer more frequent smaller meals, encourage activity during day, discourage naps/caffeine later in day, teach to reframe/refute negative thoughts, give more time/directions for ADL
Post partum blues: 1-4days. TRT: reassurance, support. depression: 2weeks – 12months. TRT: SSRI’s and therapy Psychosis: begins 2-3 das after delivery. TRT: hospitalization, antipsychotics
Treatment for seasonal affective disorder: SSRI’s and light
SSRI (Prozac, Zoloft, Lexapro, celexa): dry mouth, sweating, weight change, mild nausea, loose stool, headache, sexual dysfunction. NEED to taper off, assess for serotonin syndrome. Take 2- weeks. Remain on it for 6-9 months. Safe in overdose. DO NOT MIX WITH MAOI’s within 14 days, or St. John’s Wort!!!! Serotonin syndrome: agitation, diarrhea, heavy sweating, fever
TCA: 2-6 weeks. SE: sedating, OH, tachycardia, dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, retention, cardiac toxicity in overdose. MORE ANTICHOLINERGIC EFFECTS
MAOI’s: used if SSRI/TCA nonresponsive. And for dysthymia. AVOID= sherry, red wine, liquers, MSG, sauerkraut, fermented/smoked meat, liver, all cheese, overly ripe fruit, chocolate, dietary restriction for 14 days after discontinuing
Bipolar: one or more manic episode w/o depression. More in female, family history. DSM 5 criteria: Increased self-esteem, grandiosity, decreased need for sleep, increased pressured speech, flight of ideas, racing thoughts, distractibility, increased activity, agitation, excessive involvement in pleasurable activities, lability of mood w/ rapid shifts to depressed mood.
Bipolar 1 = 1 major depression + mania Bipolar 2= 1 major depression – HYPOmania
Interventions: at risk for injury, so safety. Need consistency w/ short concise statements. Remain neutral/avoid power struggles , decrease environmental stimulil
- provide high calorie fluids/finger foods, monitor I&O and VS. Frequent rest periods, observe for destructive behavior, redirect, teach relaxation, evaluate consequences.
Relapse prevention: prodromal phase is where early signs and symptoms appear. Trigger education, teach to get help early, manage life stress, teach families to identify recurrence, stay on meds, MOST COMMON relapse b/c of meds
Affect is described as: broad, restricted, blunted, flat, inappropriate (CH 6)
Coping mechanisms Regression: r/t to information-processing problems and expenditure of large amounts of energy in efforts to manage anxiety, leaving little for ADLs. Projection: effort to explain confusing perceptions by assigning responsibility to someone/thing Withdrawal: r/t to problems establishing trust and preoccupation with internal experiences Denial: allows person time to gather internal/external resources then adapt to stressor gradually
Antipsychotic meds (not addictive, lower abuse potential, safe in overdose, can be given IM): latuda, abilify, Risperdal, Seroquel, Zyprexa used more/cost more, metabolic syndrome(wt gain, diabetes, increased lipids, cardiovascular probs, sedation, dizziness, constipation) clozaril causes agranulocytosis.
Prolixin used for disorganized thoughts. Cogentin used for antiparkinsonian agent to relieve drug-induced EPS like tremor
Typical (dopamine antagonists): Haldol, prolixin. More side effects(High EPS, low anticholingergic, thrombocytopenia), more monitoring. Atypical: high anticholinergic effects and low EPS effects, weight gain (baseline weight important) takes about 1 week to work Clozaril: risk for agranulocytosis, fever, elevated BP
Extrapyramidal symptoms: muscle rigidity, tremors, akathisia, drooling, shuffling gait, dystonia/ oculogyrus. Stooped posture, flexed at elbows and wrists, masklikek face EPS IS REVERSIBLE: decreased dosage, change to dif meds, administer anticholinergic (Cogentin/artane) or benadryl(antihistamine) or dopamine agonist (symmetrel)
Tardive dyskinesia: permanent, no treatment. Involuntary mouth movements, foot tapping, pill rolling. On abnormal involuntary movements, 2+ indicates TD.
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome: rare, fatal, discontinue high potency drugs, rehydrate, renal dialysis, fever reduction, pharm (dantrolene, bromocriptine). Symptoms: fever, tachycardia, muscle rigidity, tremor, stupor, increased CPK.
Stages of relapse:
Overextension: overwhelmed. Anxiety intensified, more effort to perform usual activities, decreasing performance efficiency, easy distractibility Restricted consciousness: previous anxiety + depression. Disinhibition: first appearance of psychotic features. Resembles hypomania. Hallucinations and delusions pt cannot control. Psychotic disorganization: above intensify, loss of control. 1)destructuring of external world
2)destructuring of self 3)loudly psychotic Psychotic resolutions: in hospital, medicated, but still experiencing psychosis. Robotic answers, following orders.
MM-SMAT can help patient self-report symptoms.
Anxiety
Mild- part of day-to-day living, can motivate learning. Increased perceptual field Mod – focus only on immediate concern, perception narrows Severe – significant reduction in perception. Behavior aimed to relieve anxiety. Panic – awe, dread, terror, frightened, paralyzed.
Regulation of anxiety is related to
Pharm for GAD & Panic: SSRI first in line. Benzodiazepines: short term, addicting, need to taper off. Buspar: takes time, non-benzo anxiolytic
OCD treatment: SSRI’s like Prozac(fluoxetine)
Depersonalization: feeling of being detached from one’s body/thoughts Derealization: body has unreal/strange quality
PTSD: more than one month after traumatic event.
Panic attack DSM 5= palpitation, sweating, trembling, SOB, feeling of choking, chest pain, nausea, dizzy/faint, de-realization/depersonalization, numbling/tingling, chills/hotflashes
Substance abuse
Criteria: at least 2 in 12month period, taken in larger amt than intended,
AUDIT-C test = 1) how often, 2)how many, 3)6+ drinks? Men 4+ is positive. B-DAST: quickest drug abuse screening tool. 6+ is abuse problem. SBIRT: improve early identification of people who are overusing, abusing, or dependent on alcohol or other substances.
Alcohol withdrawal: increased HR, BP, T, diaphoresis, confusion, anxiety, hand tremors, N&V, muscle cramps, impaired appetite, intestinal cramps. TRT: long acting benzo. Nutrition: B12, magnesium, multi vitamin, folate. Antiseizure med (Neurontin)
Long term meth effect looks similar to Parkinson’s or alzheimer’s
Meth withdrawal similar to Depression
Withdrawal from opiate & stimulants are uncomfortable
Parietal lobe = processing center of touch/temp/pain/proprioception/visuospacial
Emotional brain = limbic + frontal (rewards+punishment) amygdala – generate emotions, opiate receptor, responses to fear. STORES memories of phobia/ ptsd, and coordinate emotion with physical symptoms! Bigger = bipolar. Hippocampus = immune system, memory storage long term. Controlls the RECALL of event stores it in memory (PTSD). Decreased = depression Thalamus = sensory input
Excitatory = dopamine, norepinephrine, “learned excitatory” =glutamate(increased by caffeine) Inhibitory = serotonin, GABA, melatonin ) <- these two work together to manage overall excitation
Dopamine = motor, motivation, cognition, regulate emotion, rewards, pleasure
Glutamate = increased by caffeine. “learned anxiety” if there’s too much.
Norepinephrine = attention&vigilance, mood&reward Tricyclics decrease NE activity
Serotonin= allows you to stop when you achieved what you need. Inhibition, calmness, temp&sleep regulation, pain perception
Schizophrenia = related with influenza, born in late winter/early spring. !!! ventricle enlargement, prefrontal cortex not fully developed, brain volume decreased of gray&white matter, lesions in frontal/temporal/limbic regions, decreased blood flow to prefrontal cortex, smaller thalamus. TOO MUCH DOPAMINE, late adolescence.
Anxiety – dysregulation of GABA (lower) OR too much norepinephrine, which has treatment which is TCA, too little serotonin, too much glutamate
Depression = decreased hippocampus, excess cortisol (highest at 8am, 4pm but not occur at depressed people)
Deficiency of GABA = mania?
Alcohol,meth,cocain users = understimulated reward centers
TCA blocks norepinephrine & serotonin reuptake sites.
Nore & epi destroyed by MAO
Dopamine addiction feeds pleasure pathway regardless of drug used
Opiate increase neuronal firing rate of dopamine cells. COcain inhibit reuptake of dopamine
Neuroplasticity = brain’s ability to adapt, compensate for injury
Involved with memory = frontal, parietal, temporal. Amygdala, hippocampus, temporal.
Legal/ethical/spiritual/cultural
APOWW = police apprehension w/o warrant
Order of Protective services (OPC) = within 24hrs of admission. Probable cause in 72. Meantl health hearing in 2wks.
Patient’s rights: communicate, personal effects, religion, contractual relationships/wills, education, habeas corpus, independent exam, privacy, right to refuse, least restrictive setting, informed consent
Confidentiality exception!!! = emergency, court-ordered, criminal/commitment procedngs, protect 3rd parties, child custody disputes, state law, child abuse proceedings.
Informed consent includes = procedure, pros/cons, treatment alternatives, why it is most appropriate, possible outcomes, time for consideration, permission.
Insanity defense = not guilty by insanity. Guilty but mentally ill.
Medication cautions:
Lithium – watch for electrolyte and sodium balance
Clozapine (clozaril) 2nd gen atypical antipsychotic – watch for agranulocytosis
Fluoxetine (Prozac) – watch for acetylcholine block
Venlafaxine (Effexor) – watch for heightened feeling of anxiety
Mood stabilizers, anticonvulsant types– carbamazepine (tegretol), iamotrigine (lamictal), gabapentin (Neurontin), valproate (Depakote)
Antipsychotic meds’ overdose is a concern for: parkinson’s, weight gain, hyperlipidemia, diabetes
Phenothiazine – causes EPS, and photosensitivity!!, OH so keep supine then slowly change position
Benzodiazepines = Chlordizepoxide HCl (Librium), Alprazolam (Xanax), corazepate dipotassium (Tranxene), Lorazepam (Ativan) !!! don’t drink alcohol, or depressants, taper off slowly, short term only.
Non-benzo
Buspirone (Buspar) = SE is dizziness. SHORT TERM USE, takes 2-3weeks to work. Zolpidem (Ambien) = daytime drowsiness. Give with food 1-1 before bedtime!
MAO inhibitors = Isocarboxazid (marplan), Phenelzine sulfate (Nardil), tranylcypromine sulfate (parnate), selegiline (Eldepryl) = tyramine watch out [cheese, red wine, beef chicken liver, chocolate, soy sauce, yogurt, yeast, beer]
TCA = Imipramine (tofranil), Amitriptyline (Elavil), Desipramine (Norpramin), Nortriptyline (Aventyl), Protriptyline (Vivactil), Matprotiline (Ludiomil) = Strong anticholinergic effects such
Psychoanalytic of Id/Ego/Superego = explains defense mechanism, focus on unconscious Interpersonal theory = Sullivan. “self system” of change agents of nurses
Crisis = stabilize, decrease risk factors, safety Acute stage = remission, focus on symptoms, maladptive coping, symptom reduction
Intimate space = up to 18 inches. Personal = 18in to 4ft social = 9-12ft public = 12+
Group
Forming = introduction, expectations, rules/logistics, superficial talk, leader more directive, members want to fit in
Storming = conflict, struggle for control, subgroups, trust or not, conflict bound to happen, can help grow/change group,
Norming = cohesive, increased understanding, refocus on goals, free to self-disclose
Performing = Team, more depth and self-disclosure, problem solving, solutions emerge, roles fulfilled and flexible, leader becomes more of a consultant
Termination = group vs individual, feelings of separation, review, closure, some regression
Altruism – concern for others, want to help. Universality – others experience similar things Instillation of hope – increasing hopefulness Imparting information – receiving didactic info and advice Corrective reenactment – alter previously learned experience catharsis – opportunity to express feelings previously unexpressed Group cohesion – attraction of member for group and other members Interpersonal learning – ability to engage in WIDER RANGE of interpersonal exchanges, understanding of responsibilities and complexity of interpersonal relationships
IQ
Below 20 – profound retardation with only basic communication and need assistance 20-34 = severe, master basic skills of living 35-49 = moderate, need some supervision 50-69 mild, can live with on own with community support 70-79 = borderline,
Antipsychotics helpl with tantrums & aggression SSRI help treat anger and compulsive behavior
ADHD treatment = eye convergence (ADD only), omega3 fatty acid, exercise, cut out artificial food
Major depression in children may seen as = irritable, aggressive behavior, hard time communicating feelings. 2+ weeks
Crisis/aggression
For retraint = obtain physician’s order, one staff member designated to communicate w/ pt and staff, identify
Psych Final Exam Notes
Course: Mental Health Nursing (NUR 3328)
University: Baylor University

- Discover more from: