- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Completed FL2020 12.9.2 Lab - Configure IPv6 Addresses on Network Devices
Course: Network Components (IST 1224)
5 Documents
Students shared 5 documents in this course
University: Hinds Community College
Was this document helpful?

Lab - Configure IPv6 Addresses on Network Devices
Topology
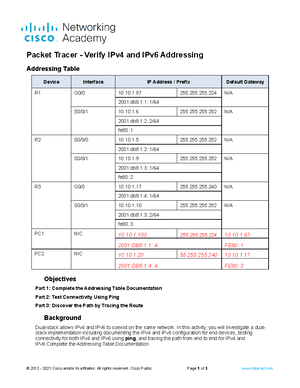
Addressing Table
Device Interface IPv6 Address Prefix Length Default Gateway
R1 G0/0/0 2001:db8:acad:a::1 64 N/A
R1
G0/0/1 2001:db8:acad:1::1 64 N/A
S1
PC-A NIC 2001:db8:acad:1::3 64 fe80::1
PC-B NIC 2001:db8:acad:a::3 64 fe80::1
Objectives
Part 1: Set Up Topology and Configure Basic Router and Switch Settings
Part 2: Configure IPv6 Addresses Manually
Part 3: Verify End-to-End Connectivity
Background / Scenario
In this lab, you will configure hosts and device interfaces with IPv6 addresses. You will issue show
commands to view IPv6 unicast addresses. You will also verify end-to-end connectivity using ping and
traceroute commands.
Required Resources
1 Router (Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
1 Switch (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
2 PCs (Windows with terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term)
Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
Ethernet cables as shown in the topology
Note: The Gigabit Ethernet interfaces on Cisco 4221 routers are autosensing and an Ethernet straight-
through cable may be used between the router and PC-B. If using another model Cisco router, it may be
necessary to use an Ethernet crossover cable.
2013 - 2021 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Page 1 of 4www.netacad.com