- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
OB Concept Map 2 Olivia Jones
Course: Parent Child Health (PCH 101)
9 Documents
Students shared 9 documents in this course
Was this document helpful?

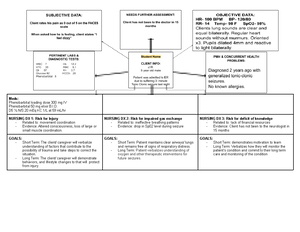
S&S:
Hypertension- Nausea - Pain; headache and epigastric -
Visual changes - Facial Edema - Pitting dependent edema-
Diaphoresis
MEDS:
LR 1000mL at 125mL/Hr
Magnesium sulfate 6g in 1000mL at 200mL/hr
LABS & TEST:
Platelets 98 RBC 5 MCH 28 MCHC 12 Creatinine 2.6 BUN
32 ALT 40 AST 42 LDH 220 Triglycerides 180 Creatinine
clearance 154
NURSING DX 1: Fluid volume deficit
- Related to: preeclampsia
- Evidence by: sudden weight gain, increased
BP and edema
NURSING DX 2: At risk for maternal injury
- Related to: seizures
- Evidence: hypertension and proteinuria
NURSING DX 3: Acute pain
- Related to: headache
- Evidence by: Patient rates the pain level as 5
out of 10
GOALS:
- Short Term: Patient is normovolemic as
evidenced by urine output, edema and BP
- Long Term: Patient verbalizes understanding of
the causing factors essential to correct fluid
deficit.
GOALS:
- Short Term: Patient will remain calm
- Long Term: Client is safe and injury free in the
event that she does experience a seizure
GOALS:
- Short Term: The patient demonstrates the use
of appropriate diversional techniques and
relaxation skills.
- Long Term: Patients well-being will improve
and pain level will decrease upon re-
evaluation.