- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Chloroquine Active Learning Template
Course: Pharmacology (NUR304)
48 Documents
Students shared 48 documents in this course
University: Immaculata University
Was this document helpful?

ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES THERAPEUTIC PROCEDURE A7
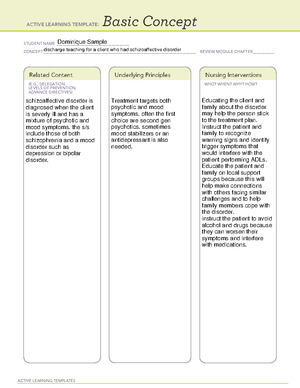
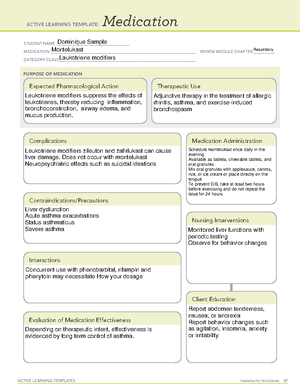
Medication
STUDENT NAME _____________________________________
MEDICATION __________________________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER ___________
CATEGORY CL ASS ______________________________________________________________________
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE:
PURPOSE OF MEDICATION
Expected Pharmacological Action
Complications
Contraindications/Precautions
Interactions
Medication Administration
Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness
Therapeutic Use
Nursing Interventions
Client Education
Dominique Sample
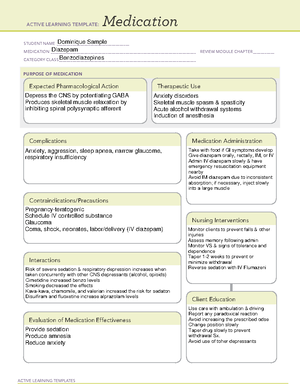
Chloroquine
Infection
Antimalarial
The exact pharmacologic action is unkown,
but is is believed that it kills erythrocytic
marlia parasites by preventing heme
conversion in the infective organism.
For clients traveling to regions of the world with
malaria, take 500mg tablets once daily
beginning one to two weeks before traveling and
continue four weeks after leaving the country
containing malaria parasites.
Acute attacks are treated by giving 1g of the
drug orally. Then a smaller dose of the drug is
giving 6, 24, and 48 hours later.
Doses for children are based on weight.
Give at least four hours before or after anti-acids
or laxatives for adequate absorption.
Give with food to prevent GI effects.
No known interactions
Liver disease
Pregnancy and lactation
Allergy to drugs related to chloroquine.
History of visual changes caused by drugs related to
chloroquine.
Optic neuritis or psoriasis.
Treats chloroquine-sensitive malaria caused by chloroquine-sensitive malaria. Combination
with primaquine is necessary to cure malaria caused by two of the parasites.
Prophylaxis for malaria in regions where chloroquine resistance is not widespread.
Treats amebiasis.
Second-line therapy to treat rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.
Monitor for and report any
visual symptoms.
Monitor for and report severe GI
symptoms.
Patient is cured of infection. RA and SLE symptoms are
lessened
Wearing sunglasses may help
minimize visual effects.
Report any visual changes to
provider.
Take just before or following a
male to minimize GI symptoms