- Information
- AI Chat
This is a Premium Document. Some documents on Studocu are Premium. Upgrade to Premium to unlock it.
Was this document helpful?
This is a Premium Document. Some documents on Studocu are Premium. Upgrade to Premium to unlock it.
Medication Ibuprofen - ati med template
Course: Maternity Nursing Care
236 Documents
Students shared 236 documents in this course
University: Keiser University
Was this document helpful?
This is a preview
Do you want full access? Go Premium and unlock all pages
Access to all documents
Get Unlimited Downloads
Improve your grades
Already Premium?

ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES THERAPEUTIC PROCEDURE A7
Medication
STUDENT NAME _____________________________________
MEDICATION __________________________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER ___________
CATEGORY CL ASS ______________________________________________________________________
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE:
PURPOSE OF MEDICATION
Expected Pharmacological Action
Complications
Contraindications/Precautions
Interactions
Medication Administration
Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness
Therapeutic Use
Nursing Interventions
Client Education
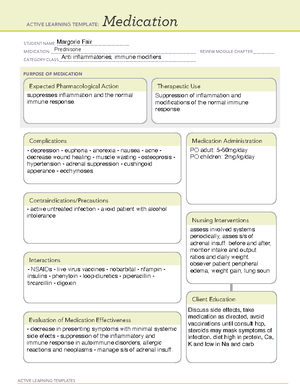
Margorie Fair
Ibuprofen
NSAIDs
Ibuprofen resulted effective in several pain conditions in children such as
musculoskeletal pain, ear pain and acute otitis media, toothache and the
inflammatory disease of the oral cavity and pharynx. The drug is a
reasonable and efficacious alternative in postoperative pain, including
tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy.
Ibuprofen is the most widely used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory
drug (NSAID) for the treatment of inflammation, mild-to-moderate
pain and fever in children, and is the only NSAID approved for use in
children aged ≥3 months.
bleeding gums.
chest pain.
constipation.
cough or hoarseness.
depression.
dry mouth.
fever with or without
chills.
frequent urination.
stomach pain, indigestion or heartburn, and child may feel sick
(nausea) or be sick (vomit), diarrhea
Ibuprofen can be taken as liquid or chewable tablets. To
give the correct dose, you need to know child's weight.
You also need to know how much ibuprofen is in a tablet,
teaspoon (tsp), 1.25 milliliters (mL), or 5 mL of the
product you are using. You can read the label to find out.
For chewable tablets, the label will tell you how many
milligrams (mg) are found in each tablet, for example 50
mg per tablet.
For liquids, the label will tell you how many mg are found
in 1 tsp, in 1.25 mL, or in 5mL. For example, the label
may read 100 mg/1 tsp, 50 mg/1.25 mL, or 100 mg/5 mL.
It is contraindicated in neonates and in children with wheezing and
persistent asthma and/or during varicella. Most of the analysed
studies reported adverse events when ibuprofen was being used for
fever symptoms or flu-like syndrome. Ibuprofen should not be used
as an antipyretic, except in rare cases. Active peptic ulcer;
hypersensitivity. Neonates with congenital heart disease, suspected
necrotising enterocolitis and active bleeding (parenteral).
Be aware that patient may be at increased risk of CV
event, GI bleeding, monitor accordingly.
Administer drug with food or after meals if GI upset
occurs.
Arrange for periodic ophthalmologic examination during
long-term therapy.
Discontinue drug if eye changes, symptoms of hepatic
impairment, or renal impairment occur.
Institute emergency procedures if overdose occurs:
Gastric lavage, induction of emesis, and supportive
therapy.
Acetaminophen, Children’s Tylenol
Albuterol
Atarax (hydroxyzine)
baclofen
Bactroban (mupirocin topical)
Benadryl (diphenhydramine)
Benadryl Allergy (diphenhydramine)
Keppra (levetiracetam)
Pulmicort Respules
(budesonide)
Zantac (ranitidine)
Zyrtec (cetirizine)
Carefully read all of the instructions on the label before
giving child medicine.
Make sure to know the strength of the medicine in the
bottle that is purchased.
Use the syringe, dropper, or dosing cup that comes with
your child's liquid medicine. You can also get one at your
local pharmacy.
Make sure you are using the right unit of measurement
when filling medicine. You may have the option of
milliliters (mL) or teaspoon (tsp) dosing.
If you are not sure what medicine to give your child, call
your provider.
Ibuprofen may also cause a serious type of allergic reaction called anaphylaxis.
Although this is rare, it may occur often in patients who are allergic to aspirin or other
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Anaphylaxis requires immediate medical
attention. The most serious signs of this reaction are very fast or irregular breathing,
gasping for breath, wheezing, or fainting. Other signs may include changes in skin
color of the face; very fast but irregular heartbeat or pulse; hive-like swellings on the
skin; and puffiness or swelling of the eyelids or around the eyes. If these effects occur,
get emergency help at once .