- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Chlorpromazine - Drug template done during the semester
Course: Nursing (NUR 340)
262 Documents
Students shared 262 documents in this course
University: Long Island University
Was this document helpful?

ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES THERAPEUTIC PROCEDURE A7
Medication
STUDENT NAME _____________________________________
MEDICATION __________________________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER ___________
CATEGORY CL ASS ______________________________________________________________________
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE:
PURPOSE OF MEDICATION
Expected Pharmacological Action
Complications
Contraindications/Precautions
Interactions
Medication Administration
Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness
Therapeutic Use
Nursing Interventions
Client Education
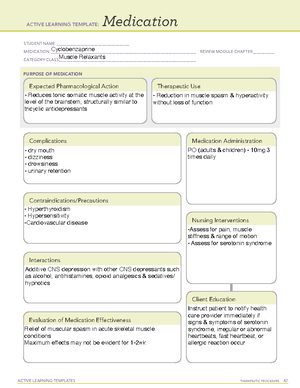
Chlorpromazine
Antipsychotics
Block several CNS and non-CNS receptors
- give oral dose with food and/or full glass of
water to prevent GI effects
- have client swallow sustained-release form
whole
- give IM injection in large muscle, rotate sites
- keep client recumbent for 30 minutes after IM
or IV dose due to possible hypotension
- IV form incompatible in solution with multiple
drugs
- give IV bolus no faster than 1 mg/minute
- CNS depressants increase sedation
- antacids and antidiarrheals - space 2 hours from
chlorpromazine administration due to poor absorption
- decreased blood level of antiseizure drugs
- allergy to phenothiazine antipsychotic drugs
- alcohol withdrawl
- bone marrow suppression
- CNS depression
- pregnancy and lactation
- respiratory disease
- glaucoma
- diabetes mellitus
- hypertension
- prostatic hypertrophy
- thyroid, cardiac, liver disorders
Akathisia: within 2 months of therapy
Parkinson-like symptoms: within first month of therapy
Acute dystonia: hours to days following first dose
Tardive dyskinesia: months to years after therapy begins
- Anticholinergic effects: dry mouth, constipation, urinary retention, blurred vision, tachycardia
- Suppressed sexual drive, erectile dysfunction
- Severe dysrhythmias
- Dermatitis, photosenitivity when exposed to sunlight
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome - high fever, rigidity, VS instability, loss of consciouness
- suppresses symptoms of schizophrenia
- acute manic phase of bipolar disorder
- relieves nausea/vomitting
- intractable hiccups
- treat with beta blocker or benzodiazepine
- possibly switch to a low - potency antipsychotic
- treat on short term basis with anti-parkinson drugs
- be prepared to administer IM or IV anticholingergic
- monitor for these irreversible symptoms
- switch client to an atypical antipsychotic
- monitor for dry mouth, constipation, and urinary retention
- counsel client about sexual dysfunction
- change to diff antipsychotic
- monitor vital signs, periodic ECG, and serum potassium levels
- wear gloves when handling phenothiazines to prevent personal
dermatitis
- prepare to administer IV dantrolene and bromocriptine
- use cooling measures and antipyretics
- keep client hydrated
- give benzodiazepines for anxiety
Relieves hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized
thoughts associated with schizophrenia.
- notify provider for feelings of inner restlessness, inability to sit
still
- notify if muscle rigidity, tremors, and sluggish movements,
drooling, and shuffling gait occur
- notify for severe spasms of the neck and body
- notify if involuntary movements of tongue, face, limbs, trunk
begin to occur
- chew gum or suck hard candy to treat dry mouth
- increase fluids/fiber to prevent constipation
- urinate just before taking drug dose
- report symptoms
- report palpations, fainting spells, other cardiac symptoms
- wear gloves when handling phenothiazines
- avoid sun exposure, use sunscreen, wear protective clothing,
wear sunglasses
- report sudden fever immediately to provider