- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Diabetes Mellitus System Disorder Type 1 and 2
Course: fundamentals of nursing (fon101)
232 Documents
Students shared 232 documents in this course
University: Raritan Valley Community College
Was this document helpful?

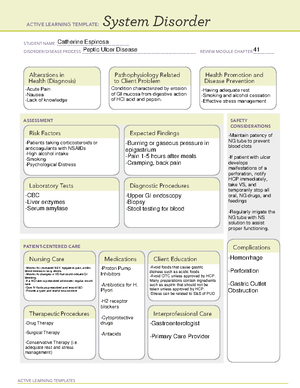
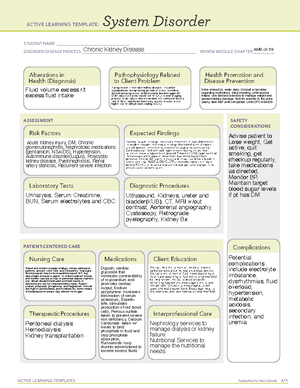
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES
System Disorder
STUDENT NAME _____________________________________
DISORDER/DISEASE PROCESS __________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER ___________
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE:
ASSESSMENT SAFETY
CONSIDERATIONS
PATIENT-CENTERED CARE
Alterations in
Health (Diagnosis) Pathophysiology Related
to Client Problem Health Promotion and
Disease Prevention
Risk Factors Expected Findings
Laboratory Tests Diagnostic Procedures
Complications
Therapeutic Procedures Interprofessional Care
Nursing Care Client EducationMedications
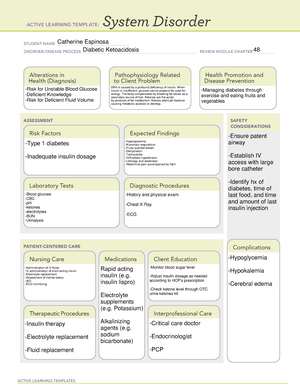
Catherine Espinosa
Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 and Type 2
48
-Lack of knowledge
-Hyperglycemia
-Hypoglycemia
-Recording of I&O
-Maintain blood glucose levels at normal or
near-normal levels
-Assess ability of patients and caregivers for
administering insulin.
-Assess patient's response to insulin therapy.
-Regular bathing with emphasis to foot care to
prevent infection.
-ECG
-Dental examination
-Neurological examination
-Fasting blood glucose
-Urinalysis
-BUN and Creatinine
-DM1: autoimmune disorder in which body develops
antibodies against insulin and/or the pancreatic beta cells
that make insulin.
-DM2: resistance to insulin action, aka, adult onset
diabetes or non insulin dependent diabetes. Risk factors
that contribute to DM 2: Obesity; Having a family hx of DM2
-Polyuria
-Polydipsia
-Polyphagia
-Sudden vision changes
-Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet
-Self monitoring of blood glucose
-Increase level of exercise
-Eating a healthy balanced diet by including fruits,
vegetables and whole grains
-Genetic predisposition
-Obesity
-Older Age
-Inactivity
-Allergic reaction
to insulin
-PVD
-Prolonged wound
healing
-PCP
-Dietician
-Physical Therapist
-Occupational Therapist
-A balanced program of exercise and rest can help
keep blood sugar level stable.
-Check blood sugar level before and after exercise.
-Always carry a carbohydrate snack (like crackers)
to eat if feeling weak.
-Advise patients to inspect feet daily and avoid
going barefoot.
-Insulin
-Enteric-coated
aspirin
-ACE inhibitors
-Angiotensin 2
receptor blockers
-Antihyperlipidemic
drugs
-Oral
Hypoglycemics
-Drug Therapy
-Nutrition Therapy
-Exercise Therapy
-Potential increase
of infection and
necrotic ulcers
which can lead to
amputations.
-Neuropathy
-Hypotension
-Muscle wasting
-Cardiovascular
disease