- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Chlorpromazine Medication outline
Course: Pharmacology for Professional Nursing (NUR2474)
296 Documents
Students shared 296 documents in this course
University: Rasmussen University
Was this document helpful?

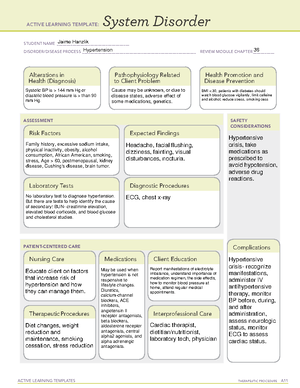
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES THERAPEUTIC PROCEDURE A7
Medication
STUDENT NAME _____________________________________
MEDICATION __________________________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER ___________
CATEGORY CL ASS ______________________________________________________________________
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE:
PURPOSE OF MEDICATION
Expected Pharmacological Action
Complications
Contraindications/Precautions
Interactions
Medication Administration
Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness
Therapeutic Use
Nursing Interventions
Client Education
Chlorpromazine
Antipsychotic/antiemetic
ACTION: Depresses cerebral cortex, hypothalamus, limbic
system, which control activity, aggression; blocks
neurotransmission produced by DOPamine at synapse;
exhibits a strongadrenergic, anticholinergic blocking action;
mechanism for antipsychotic effects is unclear
Psychosis
Adult: PO 10-50 mg q1-4hr initially then increase
up to 2 g/day if necessary
IM 1050 mg q1-4hr, usual dose 300-800 mg/day
Geriatric: PO 10-25 mg daily-bid, increase by
10-25 mg/day q4-7days, max 800 mg/day ?
Nausea and vomiting
Adult: PO 10-25 mg q4-6hr prn;
IM 12.5-25 mg q3hr prn, then 25-50 mg q6-8 hr
prn if no hypotension, max 400 mg/day; IV 25-50
mg daily-qid
Increase: CNS depression— other CNS depressants, alcohol, barbiturate anesthetics, antihistamines, sedatives/hypnotics, antidepressants
Increase: toxicity— EPINEPHrine Increase: agranulocystosis— antithyroid agents
Increase: effects of both products— β -adrenergic blockers, alcohol
Increase: anticholinergic effects— anticholinergics, antidepressants, antiparkinsonian agents, MAOIs
Increase: valproic acid level Decrease: seizure threshold— anticon - vulsants
Decrease: absorption— aluminum hydroxEENT: ide, magnesium hydroxide antacids, cimetidine Decrease: antiparkinson activity— levodopa, bromocriptine
Decrease: serum chlorproMAZINE— lithium, barbiturates
Decrease: anticoagulant effect— warfarin
Drug/Herb:
Increase: CNS depression— kava, chamomile, hops, valerian Increase: anticholinergic effect— jimson weed, scopolia Drug/Lab Test Increase: hepatic studies
Decrease: WBC, platelets, Hgb/Hct False positive: pregnancy tests, PKU False negative: urinary steroids, 17-OHCS
CONTRAINDICATIONS: Children <6 mo, hypersensitivity, circulatory collapse, liver damage, cerebral
arteriosclerosis, coronary disease, coma
Precautions: Pregnancy, breastfeeding, geriatric patients, seizure disorders, hyper - tension, hepatic/cardiac disease,
prostatic enlargement, Parkinson’s disease, pulmonary disease, severe hypo/hypertension, blood dyscrasias, brain
damage, bone marrow depression, alcohol/barbiturate withdrawal, closed-angle glaucoma
Black Box Warning: Dementia; increased mortality in geriatric patients with dementia-related psychosis
SIDE EFFECTS
CNS: EPS: pseudoparkinsonism, akathisia, dystonia, tardive dyskinesia, seizures, headache, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, dizziness
CV: Orthostatic hypotension, hypertension, cardiac arrest, ECG changes, tachycardia Blurred vision, glaucoma, dry eyes
ENDO: SIADH
GI: Dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, constipation, diarrhea, cholestatic jaundice, weight gain
GU: Urinary retention, enuresis, impotence, amenorrhea, gynecomastia, breast engorgement
HEMA: Anemia, leukopenia, leukocytosis, agranulocytosis
INTEG: Rash, photosensitivity, dermatitis
RESP: Laryngospasm, dyspnea, respiratory depression
SYST: Death in geriatric patients with dementia
USES: Psychotic disorders, mania, schizophrenia, anxiety,
intractable hiccups in adults, nausea, vomiting;
preoperatively for relaxation; acute intermittent porphyria,
behavioral problems in children, nonpsychotic, demented
patients, Tourette's syndrome
Assess:
Black Box Warning: Beers: avoid in older adults except in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, or
short-term use as antiemetic in chemotherapy; increased risk for stroke and greater rate of
cognitive decline and mortality in dementia
Mental status: AIMS assessment, orientation, mood, behavior, presence and type of hallucinations
before initial administration and monthly
Any potentially reversible causes of behavioral problems in geriatric patients before and during
therapy
I&O ratio; palpate bladder if low uri - nary output occurs, especially in geriatric patients
Monitor B/P, pulse, lying, sitting
Bilirubin, CBC, LFTs, ocular exam; agranulocytosis, glaucoma, cholestatic jaundice may occur
Respirations q4hr during initial treat - ment; establish baseline before starting treatment; report
drops of 30 mm Hg; obtain baseline ECG; Q-wave and T-wave changes
Dizziness, faintness, palpitations, tachycardia on rising
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome: hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, increased CPK, altered mental
status, for acute dystonia (check chewing, swallowing, eyes, pill rolling)
Extrapyramidal symptoms: akathisia (inability to sit still, no pattern to movements), tardive
dyskinesia (bizarre movements of the jaw, mouth, tongue, extremities), pseudoparkinsonism
(rigidity, tremors, pill rolling, shuffling gait)
Constipation, urinary retention daily; increase bulk, water in diet
Supervised ambulation until stabilized on medication; do not involve in strenuous exercise
program because fainting is possible; patient should not stand still for long periods
Increased fluids, roughage to prevent constipation
Candy, gum, sips of water for dry mouth
Therapeutic response: decrease in emotional excitement,
hallucinations, delusions, paranoia; reorganization of
patterns of thought, speech; increase in target behaviors
To use good oral hygiene; to use frequent rinsing of mouth, sugarless gum, candy, ice chips for
dry mouth
To avoid hazardous activities until product response is determined
That orthostatic hypotension occurs often; to rise gradually from sitting or lying position
To remain lying down for at least 30 min after IM inj
To avoid hot tubs, hot showers, tub baths because hypotension may occur; that during hot
weather, heat stroke may occur; to take extra precautions to stay cool
To avoid abrupt withdrawal of product or EPS may result; product should be withdrawn slowly
To avoid OTC preparations (cough, hay fever, cold) unless approved by prescriber since serious
product interactions may occur; avoid use with alcohol, increased drowsiness may occur
To use a sunscreen and sunglasses to prevent burns and photophobia
To take antacids 2 hr before or after this product
To report sore throat, malaise, fever, bleeding, mouth sores; CBC should be drawn and product
discontinued
To employ contraceptive measures
That urine may turn pink or reddish brown