- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Oxytocin (Pitocin) Med Card Complete
Course: Maternity & Women's Health (RNSG 2208)
85 Documents
Students shared 85 documents in this course
University: San Jacinto College
Was this document helpful?

ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES
Medication
STUDENT NAME _____________________________________
MEDICATION __________________________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER ___________
CATEGORY CLASS ______________________________________________________________________
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE:
PURPOSE OF MEDICATION
Expected Pharmacological Action
Complications
Contraindications/Precautions
Interactions
Medication Administration
Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness
Therapeutic Use
Nursing Interventions
Client Education
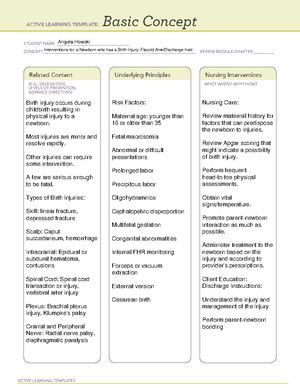
Angela Howski
Oxytocin (Pitocin)
Oxytocic Agent/labor inducer
Induce labor and aid in the delivery of the
placenta (third stage of labor), to control
postpartum bleeding
Always admin. through a pump
(piggyback). Standar
concentrations typically range from
10-30U in 500-1,000mL. Infusions
start at 1mU/min and are titrated
up by 1-2mU/min every 30-60min,
depending on response.
Acetaminophen, chlorpheniramine, dextromethorphan,
phenylephrine, guaifenesin, articaine, epinephrine, brompheniramine,
carbetapentane, dextromethorphan, bupivacaine, pyrilamine,
carbinoxamine, carboprost tromethamine, codine, dopamine,
hydrocodone, midodrine, misoprostol, methohexital
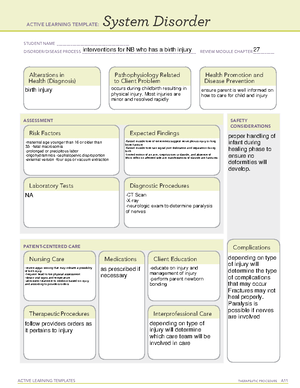
fetal distress, fetal prematurity, abnormal fetal position,
placental previa, uterine prolapse, vasa previa,
cephalopelvic, cervical cancer, 2 or more uterine/cervical
surgeries, active genital herpes
Uterine tachysystole (contractions too strong), placental
abruption, postpartum uterine hemorrhage, and rupture of
the uterus.
induce/strengthen contractions, control bleeding
after childbirth, stimulate contractions in an
incomplete or threatened mischarriage
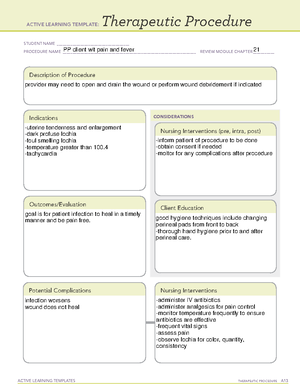
Continuous fetal and contraction mx is
required and should be reviewed every
15min and w/every change in dose. fetal mx
should be every 5min during active pushing.
Maternal HR, BP, and resp. should be
monitored every 1/2 hr to an hr and with
dose changes. Urine output should be at
least 120mL Q4hr. Intravenous intake
should not exceed 1,000mL in 8hr.
Goal: one contraction every 2-3 min lasting 80-90s
consistently, strong to palpation
Notify PCP/nurse if signs of allergic
reaction (rash, hives, itching,
red/swollen/blistered/peeling skin,
fever, wheezing, tightness in the
chest/throat, SOB, swallowing/talking,
headache/dizziness, change in
eyesight, increased bleeding, slow
heartreate
Students also viewed
- Study Guide OB test #3 - Exam 3 OB Blueprint
- OB Blueprint Test #2
- Remediation A Template Priority Actions Following Administration of Epidural Anesthesia Acute vs Chronic
- Remediation A Template merged
- Remediation A Template Gonorrhea
- Remediation B Template Pathophysology - Identify Priority Risk Factors for a Postpartum Client