- Information
- AI Chat
Help Full Cheat Sheet - Ms. Schadler
Mental Health Nursing (NSG 3233)
South College
Recommended for you
Preview text
Table of contents 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 MENTAL HEALTH OVERVIEW TREATMENT SETTINGS THERAPIES THERAPEUTIC RELATIONSHIPS AND COMMUNICATION CULTURAL CONSIDERATIONS LEGAL AND ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONS DEPRESSIVE DISORDERS ANXIETY DISORDERS AND OCD SOMATIC SYMPTOM DISORDERS AND RELATED BIPOLAR DISORDERS SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM DISORDERS PERSONALITY DISORDERS EATING DISORDERS SUBSTANCE ABUSE DISORDERS CHILDHOOD AND NEURODEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS IMPULSE CONTROL DISORDERS NEUROCOGNITIVE DISORDERS
Treatment SettingsTreatment Settings Primary Care Specialty Care Patient-Centered Medical Homes Community Mental Health Centers Psychiatric Home Care Assertive Community Treatment Intensive Outpatient Programs Partial Hospitalization Programs Emergency Care Crisis Stabilization Units General and Private Hospitals State Hospital Least Restrictive Most Acute
- Very common because many mental disorders have physical symptoms and there is less stigma.
- Psychiatrists, psychiatric nurse practitioners, psychologists, counselors, therapists, etc.
- Provides health services, social services, acute care, and chronic disease management. Patient can utilize extended hours of service outside of the usual Monday-Friday 9-5.
- Provide care on a low-cost, sliding scale. Services include emergency services, home-based services, medication prescription, therapy groups, etc.
- Provided for home-bound patients with a psychiatric diagnosis that requires the care of a nurse.
- For patients in the community with serious, persistent mental disorders that are unable to participate in traditional treatments. These teams work with the patient wherever they are at that moment.
- Programs that run Monday-Friday for about half a day. Structured activities, group therapy, and coping strategies are taught.
- Programs that run Monday-Friday for about 6 hours (slightly longer than intensive outpatient programs). Structured activities, group therapy, and coping strategies are taught.
- Primary goal is triage and stabilization. Patients may seek emergency care voluntarily, or may be brought in involuntarily for emergency evaluation.
- Provide patients with rapid stabilization and a short length of stay, usually 72 hours or less.
- Psychiatric units on a specific floor of a general hospital.
- Provide long-term care for patients with extremely serious, debilitating mental disorders and patients who can’t be stabilized in a general hospital. FREE TIRE REFINER
TherapiesTherapies Psychoanalytic Therapy: Psychodynamic Therapy: Interpersonal Therapy: Behavioral Therapy: Rational-Emotive Therapy: Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy: Brain Stimulation:
- Focuses on unconscious thoughts and feelings.
- Transference: unconscious feelings that a patient has towards a healthcare worker.
- Ex: the nurse reminds the patient of her mother.
- Countertransference: unconscious feelings a healthcare worker has towards a patient.
- Ex: the patient reminds you of someone you don’t like.
- Works best with patients who do not have severe disorders and are motivated.
- Focuses on the current issues the patient is experiencing.
- The number of sessions is predetermined at the start of therapy.
- Short-term therapy aimed at improving the severity of psychiatric symptoms by increasing satisfaction with social relationships.
- Works well with patients experiencing grief, conflicts with a significant other, and role transitions.
- Goal of changing specific behaviors without insight to the cause.
- Modeling: patient learns certain behaviors through imitation.
- Operant Conditioning: positive reinforcement to increase desired behaviors.
- Systematic Desensitization: patient is exposed to the fear little by little.
- Aversion Therapy: pairing a negative stimulus with the undesired behavior.
- Goal is to help patient identify thoughts that are irrational or inaccurate.
- Usually negative or self-deprecating thoughts.
- Recognizes that thoughts influence behavior.
- Based on cognitive psychology and behavioral theory.
- Focuses on correcting distorted thoughts and beliefs and turning them into positive thoughts and feelings.
- Correcting the distorted thoughts and feelings should have a positive impact on feelings and behavior.
- Used to treat mental disorders that don’t respond to therapy or medication.
- Electroconvulsive therapy
- Vagus nerve stimulation
- Deep brain stimulation
- Magnetic seizure therapy Psychopharmacology:
- The use of medications to treat mental disorders.
- Decreases the need for hospitalizations and improves the quality of life for patients. TREEN? E
- E goes
- i Use this page
Cultural ConsiderationsCultural Considerations Race: Ethnicity: Culture: Western Tradition: Eastern Tradition: Indigenous Culture: Cultural Syndromes: Cultural Idioms: Cultural Explanations: Distinguished visually, genetically, or anthropologically. Groups that share a common heritage, history, and worldview. Shared customs, social institutions, beliefs, practices, and values that influence behavior and thinking.
- Identity is formed in individuality.
- Independence, autonomy, and self-reliance are valued.
- Mind and body are separate entities.
- Time is linear.
- Disease has a direct cause and can be observed.
- Treatment of disease is aimed at the cause.
- Importance of right to decide, to be informed, and open communication.
- Identity is formed around family.
- Mind, body, and spirit are one entity.
- Time is circular and flexible.
- People are born into their fate, and it cannot change.
- Disease is caused by an imbalance in energy forces. *Importance of compassion, decisions on the behalf of others, and protecting loved ones from the truth.
- Identity is formed around the tribe.
- Close relationship with nature.
- Mind, body, and spirit are all related.
- Time is focused on the present.
- Disease is caused by a lack of harmony with self, others, environment, or spirit.
- Importance of contributing to the needs of the community. Symptoms that occur in a particular culture and are recognized by that culture. Ways of expressing distress in a specific culture. Ex: “I’m a nervous wreck.” Explanation of symptoms, disease, or illness understood within a particular culture. aware Reeeerier e 8 O
- J
- in ← ÷ we
Legal ConsiderationsLegal Considerations Types of Admission: Discharge Procedures: Rights of the Patient: Torts: 1 Voluntary Admission
- Informal Admission:
- Least restrictive
- Patient is not a threat to harm themself or others.
- Patient is free to leave or stay.
- Voluntary Admission:
- Patient applies in writing to admit themself to the facility.
- Patient has the right to request release from the facility.
- The provider has the right to initiate involuntary commitment. 2 Involuntary Commitment
- Court ordered admission to a psychiatric facility without consent of the patient.
- The patient must be:
- Mentally ill
- A danger to themself or others.
- Unwilling to seek voluntary treatment.
- Disability severely impacts daily life. 3 Emergency Commitment
- Temporary/emergency hospitalization.
- Usually 24 -9 6 hours. 4 Assisted Outpatient Treatment
- Court-ordered outpatient treatment.
- Often used as a preventative measure. 1 Conditional Release:
- Release with a mandatory period of outpatient treatment. 2 Unconditional Release:
- Complete termination of the patient- facility relationship. 3 Release Against Medical Advice:
- Treatment is beneficial, but patient is not a danger and may choose to leave.
- Right to treatment
- Least restrictive environment
- No unnecessary medication
- Right to privacy
- Informed consent for all treatments
- Right to attorney
- Right to refuse treatment
- Patients can deny consent and withdraw consent at any time.
- Facilities can only medicate a patient against their consent if they are an imminent threat to themself or others.
- Right to confidentiality
- Patient information cannot be disclosed without consent of the patient.
- Right to informed consent
- Patient is informed of all risks, benefits, and alternatives of treatment.
- Implied consent: less risky/invasive procedures that the patient indicates willingness.
- Ex: taking a daily medication
- Advance Directives
- Patients can express their wishes for treatment in the event of a psychiatric episode.
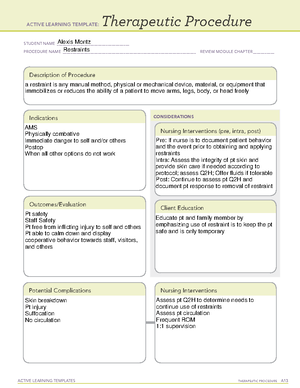
- Seclusion and Restraint
- Other methods like diversion, distraction, offering PRN medication should be attempted before seclusion/restraint. 1 Intentional Tort: intentional assault, battery, or false imprisonment. 2 Unintentional Tort: Unintended acts that cause harm - negligence and malpractice. amraam
- .
- O -
- o - o O - F- c- -
Anxiety Disorders and OCDAnxiety Disorders and OCD Levels of Anxiety: Generalized Anxiety Disorder: Social Anxiety Disorder: Panic Disorder: Specific Phobia: Separation Anxiety Disorder: Agoraphobia: Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Nursing Interventions: Medications: Non-Pharmacological Treatment: Body Dysmorphic Disorder: 1 Mild Anxiety: * A normal experience * Allows individual to grasp more information and problem-solve. 2 Moderate Anxiety: * May experience selective inattention * Clear thinking is impaired but problem- solving can still occur. * Somatic symptoms begin 3 Severe Anxiety: * Ability to grasp information is significantly impaired. Learning and problem-solving are not possible. * Somatic symptoms increase. 4 Panic * Individual is unable to process what is going down around them. * Patient could be a risk to themself or others.
- Anxiety that is out of proportion for the situation the individual is in.
- Symptoms include restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, irritability, sleep disturbances that cause significant distress.
- Severe anxiety caused by fear of doing something foolish in a social situation.
- Individuals will typically avoid social situations.
- Severe anxiety that causes frequent panic attacks with feelings of impending doom.
- Inappropriate level of anxiety about being away from a significant other for the individuals developmental level.
- May be caused by loss of a loved one, assault, immigration, etc.
- Irrational crippling anxiety/fear of an object, situation, or activity.
- Fear of being in places or situations where escaping may be difficult, or where help isn’t available. EX: being outside alone. *Obsessions: persistent thoughts that can not be dismissed from the mind. *Compulsions: behaviors the individual feels they must complete to reduce anxiety.
- Symptoms occur daily and cause distress.
- Individual is obsessed with what they perceive to be a deformed body part.
- Priority nursing intervention is to provide safety for the patient and others.
- Offer activities that provide distraction.
- Listen to the patient’s concerns.
- Reinforce reality when patient has a distorted perception.
- Provide a quiet, non-stimulating environment for patient if there is severe anxiety or panic.
- Ensure patient has adequate nutrition and fluid intake. 1 Antidepressants: (SSRIs, SNRIs, MAOIs) 2 Anti-Anxiety Drugs: Benzodiazepines, Buspirone 3 Beta-blockers, antihistamines, anticonvulsants, and antipsychotics may be used if other medications do not work.
- Therapies
- Deep brain stimulation E remarries an ran FE7¥
- O - J
- s i a O
- o
- c- -
Somatic Symptom DisordersSomatic Symptom Disorders Somatic Symptom Disorder: Illness Anxiety Disorder: Conversion Disorder: Potential Nursing Diagnoses: Medications Factitious Disorder: 1 Symptoms: * The expression of psychological stress through physical symptoms that cannot be explained by pathology. * Patient has excessive thoughts, feelings, and distress related to the symptoms. * Patients frequently seek out medical care and won’t accept psychological diagnoses for their symptoms. 2 Assess for: * Extreme preoccupation with somatic symptoms. * Somatic symptoms present for over 6 months. * Possible overmedication 3 Nursing Interventions: * Encourage independent self-care. * Encourage patient to verbalize feelings. * Educate the patient on coping mechanisms. 1 Symptoms:
- Commonly referred to as hypochondriasis.
- Extreme anxiety and worry about the possibility of having a disease or disorder.
- Somatic symptoms are mild or non- existent. 2 Assess for:
- Excessive fear surrounding health for over 6 months.
- Excessive healthcare-seeking behavior or healthcare avoidance. 3 Nursing Interventions:
- Build trust with the patient.
- Encourage patient to verbalize feelings
- Educate patient on stress management techniques and alternate coping mechanisms. 1 Symptoms: *Neurological symptoms without a neurological diagnosis caused by psychological stress.
- Neurological symptoms may present as paralysis, blindness, numbness, loss of hearing or vision, etc. 2 Assess for:
- Alterations in motor or sensory function.
- Assess recent stress levels.
- Some patients may experience extreme anxiety, while others seem indifferent (la belle indifference). 3 Nursing Interventions:
- Ensure safety of the patient
- Encourage the patient to identify what may have triggered the conversion.
- Educate the patient on stress management techniques. 1 Factitious disorder imposed on self:
- Previously known as Münchausen syndrome
- Patient reports falsified physical or psychological symptoms.
- Patient may intentionally harm themself.
- Done with the intention of gaining attention or sympathy, not personal gain. 2 Factitious disorder imposed on another:
- An individual purposely causes illness or injury to a vulnerable person.
- Ineffective coping
- Anxiety
- Powerlessness
- Social isolation *Altered family processes
- No medications have been approved for use specifically for somatic symptom disorders, but some antidepressants and anti-anxieties may be used off-label. damn After EEEI HEREERnone of It . . o -
- o - o- l
- O - tf " 0 " I I ←
Schizophrenia spectrum disordersSchizophrenia spectrum disorders Schizophrenia: Schizotypal Personality Disorder: Schizoaffective Disorder: Schizophreniform Disorder: Delusional Disorder: Brief Psychotic Disorder: Assessment: Nursing Interventions: Treatment:
- Sudden onset of hallucinations, delusions, disorganized speech, or disorganized behavior.
- Lasts between 1 day and 1 month.
- Delusions that last at least 1 month.
- The delusions usually are not severe enough to impair functioning.
- Behavior is not usually strange or bizarre.
- Patient has all the same symptoms of schizophrenia, but only lasts 1- 6 months.
- Usually does not impair social or occupational functioning.
- The patient meets the criteria for schizophrenia as well as bipolar or depressive disorder.
- Psychotic thinking or behavior that lasts for at least 6 months.
- Typically presents between age 15 and
- Hallucinations, delusions, disorganized speech or disorganized behavior.
- Symptoms significantly impair normal daily functioning.
- Patient has impairments surrounding their personality.
- Delusions, fears, and difficulties surrounding the formation and maintenance of relationships.
- Positive symptoms: characteristics that should not be present.
- Hallucinations, delusions, alterations in speech/behavior
- Negative symptoms: characteristics that should be present that are not.
- Blunted/flat affect, poverty of thought/speech, anergia (lack of energy), anhedonia (lack of pleasure).
- Delusions
- Alterations in speech
- Alterations in perception
- Difficulties with personal boundaries
- Alterations in behavior
- Disturbed sensory perception
- Risk for violence
- Impaired communication
- Altered thought processes
- Provide a structured environment
- Ask the patient about their hallucinations/ delusions.
- Tell the patient you do not hear/see anything, but believe that they do.
- Focus conversations on reality.
- Identify what triggers symptoms.
- Assess for paranoid delusions, as they can lead to violence against self or others.
- Encourage the patient to participate in group activities and work on building social skills.
- Maintaining safety of the patient and other patients is the always the most important focus.
- First-generation antipsychotics
- Second-generation antipsychotics
- Antidepressants
- Mood stabilizers
Nursing Diagnoses:
@RREhRPBPnQMnMeRPRiRfBMADorRnBno
Et
Tf
I
Personality disorders Cluster A Cluster B Cluster C Paranoid: Schizoid: Schizotypal: Antisocial: Borderline: Histrionic: Narcissistic: Avoidant: Dependent: Obsessive- Compulsive: Nursing Considerations: Treatments: Odd or eccentric behavior Dramatic, emotional, or erratic behavior Anxious, fearful, or insecure behavior
- Suspiciousness of others
- Belief that others want to harm, deceive, or exploit them.
- RN should remain neutral and direct when interacting with patient.
- Social withdrawal, emotional detachment.
- Disinterest in close relationships.
- Indifferent to praise or criticism.
- Uncomfortable with social interaction.
- Very strange behavior
- Magical thinking, odd beliefs, strange speech patterns.
- Severe social deficits.
- Perceptual distortions (misinterpreting actions of others).
- Dramatic, attention- seeking behavior.
- Extroversion
- Self- centeredness
- Difficulty forming long- lasting relationships
- Lack of empathy
- Arrogance.
- Sensitivity to criticism.
- Seeks admiration from others.
- Fear of abandonment.
- Usually will not accept treatment.
- Disregard for others.
- Exploitation of others.
- Will not accept responsibility.
- Manipulation
- Impulsivity
- Can be charming
- Instability of identity.
- Splitting behaviors
- Fear of abandonment.
- Ideas of reference.
- Manipulation
- Impulsivity
- Avoidance of social contact.
- Extreme fear of rejection.
- Feelings of inadequacy.
- Extreme anxiety in social situations.
- Intense fears of separation.
- High need to be taken care of.
- Feelings of insecurity.
- Lack of confidence in their own abilities and judgement.
- Perfectionism, orderliness, and control.
- Stubbornness
- Indecisiveness
- Often can not accomplish tasks. 1 Patients with personality disorders can create strong emotional reactions within the nurse. Ex: Attempting to create tension between staff. 2 Maintaining safety in the milieu is the highest priority.
- Patients with personality disorders are at risk for injury to self or others. 3 Maintain consistent care with the patient and maintain firm boundaries. 4 Self-assess for Countertransference reactions.
- Medications are prescribed to treat symptom manifestations.
- Antidepressants, anti- anxieties, antipsychotics, and mood stabilizers.
- Behavioral and psychotherapy is also utilized. O O O O ÷
: O and
Substance Use DisordersSubstance Use Disorders Cannabis Use Disorder: Hallucinogen Use Disorder: Inhalant Use Disorder: Opioid Use Disorder: Sedative/Hypnotic/Anti-anxiety Medication Use Disorder: Stimulant Use Disorder: Alcohol Use Disorder:
- Frequent consumption of alcohol in larger amounts or longer periods than intended.
- Unsuccessful attempts to decrease alcohol consumption.
- Continued alcohol use despite causing problems with relationships, work, etc. 1 Intoxication:
- Impaired judgement, poor muscle coordination, slurred speech, memory impairment.
- 4 mg/dL blood alcohol levels causes impaired vital signs and possible death. 2 Withdrawal:
- After 6- 8 hours, shakes begin.
- After 8-1 0 hours psychotic symptoms and perceptual distortions May begin.
- Withdrawal seizures and alcohol withdrawal delerium May occur and can cause death. 3 Treatment:
- Diazepam (Valium), chlordiazepoxide (Librium), and lorazepam (Ativan) can be given to reduce delirium and seizures.
- Use interferes with work, home life, social life, and physical health.
- Using larger amounts over long periods of time, tolerance increases. 1 Intoxication:
- Heightened sensations
- Depersonalization/derealization
- Increased appetite
- Tachycardia 2 Withdrawl:
- Within 1 week of cessation
- Irritability, anger, anxiety, depressed mood, insomnia, headache, shakiness.
- LSD, PCP, Ketamine, etc.
- Strong cravings, tolerance, difficulty maintaining obligations. 1 Intoxication:
- Paranoia
- Illusions, hallucinations, synesthesia 2 Withdrawal:
- Hallucinogen persisting perception disorder 3 Treatment:
- Antipsychotic medications and benzodiazepines.
- Glues, adhesives, aerosol sprays, paint.
- Tolerance develops, unable to maintain obligations. 1 Intoxication:
- Disinhibition, illusions, hallucinations
- Can cause death
- Heroin, prescription drugs
- Increasing tolerance, longer periods of use. 1 Intoxication:
- Drowsiness, slurred speech, impaired memory, pupil construction, respiratory depression, can cause overdose and death. 2 Withdrawl:
- Nausea, vomiting, muscle aches, fever. 3 Treatment:
- Narcan 1 Intoxication:
- Incoordination, slurred speech, impaired thinking. 2 Withdrawal:
- Hyperactivity, tremor, insomnia, agitation. 3 Overdose treatment:
- Activated charcoal, gastric lavage, vital sign monitoring.
- Amphetamines, cocaine, etc. 1 Intoxication:
- Cardiac arrhythmia, respiratory depression, dilated pupils, perspiration. 2 Withdrawal treatment:
- Antipsychotics for psychosis, diazepam for hyperactivity, bupropion for depression. renren tea restorer Er
####### i:*
- o -
RE
E i ± : =
NEURODEVELOPMENTNEURODEVELOPMENTALAL DISORDERSDISORDERS Communication Disorders: Motor Disorders: Specific Learning Disorders: Intellectual Disability: Autism Spectrum Disorder: Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder:
- Deficits in language acquisition that create impairments in communication. 1 Speech disorders:
- Problems with making certain sounds
- Child-onset fluency disorder (stuttering) 2 Receptive language disorder:
- Difficulty understanding and following directions. 3 Expressive language disorder:
- Difficulty using correct words and forming complete sentences. 4 Social communication disorder:
- Difficulty interacting socially with others. 1 Developmental Coordination Disorder:
- Impairment of motor skill development
- Motor skills do not meet the childs level of development.
- Interferes with ability of the child to perform activities of daily living. 2 Stereotypic Movement Disorder:
- Repetitive movements with no purpose.
- Hand waving, rocking, teeth grinding, head banging, etc.
- Difficulty in reading: dyslexia.
- Difficulty in math: dyscalculia
- Difficulty in writing: dysgraphia
- Children with specific learning disorders are usually put on Individualized Education Programs (IEP) at school.
- Early intervention is important to ensure the best possible outcome.
- Causes deficits in:
- Intellectual functioning: thinking, reasoning, etc.
- Social functioning: communication, emotions, etc.
- Daily functioning: ADLs, self-care, etc.
- Typically appears between birth and age
- Impacts the development of social and communication skills.
- Symptoms:
- Difficulty developing relationships
- Repetitive speech
- Hyper-reactivity to sensory input
- Extreme focus on routines
- Excessive focus on objects
- Resistance to change
- Children with autism are referred to early intervention programs.
- Pharmacological treatment can include second-generation antipsychotics and SSRIs.
- Inappropriate levels of hyperactivity, impulsiveness, and inattention.
- Symptoms:
- Poor social boundaries
- Interrupting others
- Intrusive behaviors
- Difficulty taking turns
- Symptoms must be present both at home and school before age 12.
- Symptoms can cause:
- Frustration
- Anger outbursts
- Poor school performance
- Low self-esteem
- Modeling good behavior
- Role playing
- Ignoring attention-seeking behavior
- Redirecting inappropriate behavior
- Limit setting
- Restructuring activities to meet the needs of the child. Managing Disruptive Behavior: extremeerror ere Eee
- y
- o -
- T . - M
- =
Neurocognitive DisordersNeurocognitive Disorders Delirium: Neurocognitive Disorder: Alzheimers Disease:
- Rapid onset in a short period of time
- Considered a medical emergency
- Common in older patients 1 Causes:
- Infection
- Malnutrition
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Substance use
- Medication interactions 2 Symptoms:
- Impairments of memory, thinking, judgement, and focus
- Disorientation and confusion
- Hallucinations and illusions
- Restlessness and anxiety
- Personality change 3 Assessment:
- Assess level of awareness
- Determine usual level of awareness
- Assess vital signs and potential for injury 4 Nursing Diagnoses:
- Risk for injury
- Acute confusion
- Impaired social interaction 5 Interventions:
- Identify cause of delirium
- Administer prn medications for anxiety
- Assist with nutrition and self-care needs
- Use simple and direct statements
- Maintain consistent environment/routines
- Maintain 1-on- 1 supervision at all times
- Often referred to as dementia.
- Progressive deterioration of cognitive functioning.
- Occurs over a period of months or years. 1 Causes:
- Advanced age
- Traumatic brain injury
- Genetics
- Diabetes
- Other neurological disorders 2 Symptoms:
- Memory impairments
- Inability to recognize familiar items
- Speech deficits
- Functional impairments
- Agitation
- Sundowning syndrome
- Personality change 3 Interventions:
- Monitor nutrition and weight.
- Give one direction at a time.
- Use distraction to manage behavior.
- Provide cues
- Utilize written signs
- Limit the amount of choices the patient has to make during the day.
- Progressive deterioration of memory, cognitive functions, and the ability to complete activities of daily life.
- Organized into three stages:
- Mild:
- Memory lapses
- Misplacing items
- Difficulty planning and organizing
- Moderate:
- Forgetting personal history
- Wandering and getting lost
- Personality and behavioral changes
- Severe:
- Inability to perform self-care
- Changes in physical abilities
- Difficulty communicating
- Poor awareness of surroundings
- Nursing diagnoses:
- Risk for injury
- Impaired communication
- Impaired memory
- Treatments:
- Community supports for family
- Cholinesterase inhibitors
- Prevents breakdown of acetylcholine
- Donepexil (Aricept) *NMDA receptor agonist
- Memantine (Namenda)
- Other medications may be used to control behavioral symptoms. IT REFER TE RRRRRR RRR o is o -
- o - -
- O - O - o - is . .
ANAANATOMYTOMY OFOF THETHE BRAINBRAIN Midbrain Pons Medulla Oblongata Cerebellum Frontal Lobe Parietal Lobe Occipital Lobe Temporal Lobe Thalamus Hypothalamus Pituitary Gland Third Ventricle Pineal Gland
- Thought processes
- Decision making
- Judgement
- Planning
- Insight
- Motivation
- Voluntary motor actions
- Sensory and motor actions
- Receive sensory information
- Body awareness
- Left/right orientation
- Reading, math
- Formation of concepts
- Vision
- Interpret visual images
- Visual memories
- Visual association
- Auditory
- Language comprehension
- Memory of language and speech
- Expression of emotions
- Pupil reflex
- Eye movements
- Processing for auditory pathways
- Reflex center
- Balance
- Heart rate
- Respiration rate
- Muscle contraction and coordination
- Equilibrium
- Maintains homeostasis
- Maintains heart rate and blood pressure
- Controls endocrine gland / hormones
- Regulates some hormones including melatonin
- Relays sensory and motor functions
- Regulates consciousness
- Protects brain from injury
- Transports nutrients and waste eerie . are entire
yr
= T - -
hi
Help Full Cheat Sheet - Ms. Schadler
Course: Mental Health Nursing (NSG 3233)
University: South College

- Discover more from: