- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Med Term Ch 17 - Chapter 17!! - Medical Terminology
Course: Medical Terminology (HSC 236)
38 Documents
Students shared 38 documents in this course
University: The University of Tampa
Was this document helpful?

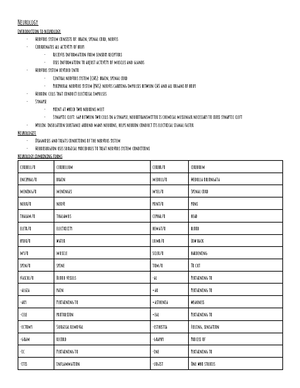
Chapter 17: otorhinolaryngology
- Otorhinolaryngology (ENT): focuses on head and neck, not just a single body system, head and neck: houses sensory organs and provides passageways for air,
food, and drinks
- Organs include: ears (hearing and balance), nose (smell and entrance for air), pharynx (carries air to larynx and food to esophagus), larynx (speech), and trachea
(brings air to lungs)
- Diagnosis and treatment of diseases and conditions aecting head and neck include: hearing, balance, swallowing, voice, neck tumors, and airway problems
- adenoid/o: adenoids, audi/o: hearing, audit/o: hearing, aur/o: ear, cochle/o: cochlea, epiglott/o: epiglottis, laryng/o: larynx (voice box), myring/o: tympanic
membrane (eardrum), nas/o: nose, ot/o: ear, pharyng/o: pharynx (throat), rhin/o: nose, sinus/o: sinus, tonsill/o: tonsils, trache/o: trachea (windpipe),
tympan/o: tympanic membrane
- gastr/o: stomach, myc/o: fungus, neur/o: nerve, py/o: pus
- -al: pertaining to, -algia: pain, -ar: pertaining to, -eal: pertaining to, -ectomy: surgical removal, -gram: record, -ic: pertaining to, -itis: inflammation,
-logist: one who studies, -logy: study of, -megaly: enlarged, -meter: instrument to measure, -metry: process of measuring, -oma: tumor or mass, -ory:
pertaining to, -osis: abnormal condition, -osmia: smell, -otomy: cutting into, -phonia: voice, -plasty: surgical repair, -plegia: paralysis, -rrhea: discharge or
flow, -rrhexis: rupture, -sclerosis: hardening, -scope: instrument for viewing, -scopy: process of visually examining, -spasm: involuntary muscle contraction,
-stenosis: narrowing
- A-: without, an-: without, de-: without, dys-: abnormal or dicult or painful, endo-: within, pan-: all, para-: beside; two like parts of a pair
- Adenoids: one of three pairs of tonsils located in pharynx (also called pharyngeal tonsils), house large number of white blood cells: protect body by removing
foreign invaders from air passing through pharynx
- Ear: responsible for hearing and equilibrium (balance), divided into: external ear, middle ear, and inner ear
- external ear: pinna (auricle) captures sound waves, funnels them into external auditory canal, sound waves strike tympanic membrane (eardrum) causing it to
vibrate
- middle ear: three tiny bones (ossicles) in middle ear: malleus, incus, and stapes (conduct this vibration across middle ear from tympanic membrane to oval
window)
- Inner ear: oval window movement initiates vibrations in fluid inside inner, vibrating fluid bends hair cells in cochlea which stimulates nerve endings,
auditory nerve sends message to brain, inner ear also contains organs for equilibrium semicircular canals
- Cochlea: part of inner ear containing hair cells responsible for hearing, shaped like a coiled snail shell
- Epiglottis: cartilage flap that sits above larynx and tips forward to cover larynx with each swallow: prevents flood or drink from entering larynx and trachea
- Larynx: commonly called voice box, located between pharynx and trachea, contains vocal cords: vibrate as air passes through them and produce sound
- Tympanic membrane: eardrum
- Nose: air enters through two nares: passes through nasal cavity into pharynx, nasal cavity: divided down middle by nasal septum, lined by mucous membrane,
air is warmed or moisturized or cleansed, houses sensory receptors for sense of smell
Students also viewed
- 1. Basic Chart - Piaget Theory of Cognitive Development I
- Med Term Ch 11 - chapter 11! - MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
- Med Term Exam 4 - exam 4 review! - MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
- Med Term Ch 2 - chapter 2!! - MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
- Med Term Exam 1 - review for exam 1 - MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
- Med Term Ch 4 + 3 - chapter 3 and 4 quiz review - MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY