- Information
- AI Chat
PEDS EXAM 1 Study Guide
Pediatric Nursing Care (MCN 354)
University of South Alabama
Related Studylists
P#1Preview text
Chapter 25 – Growth and Development of the Newborn and Infant
- Describe the difference between cephalocaudal and proximodistal development.
Cephalocaudal is the development of gross motor skills which goes head to toe
Proximodistal is the development of fine motor skill which is closest then furthest to the body
Physical Growth a. Weight - It is normal to lose 10% of body weight within first week - Should regain birthweight by 10-14 days - Birthweight should double by 4 months and triple by 1 year b. Height - Height should increase by 50% in 1 year c. Head circumference - A 10 cm gain in a year is normal d. Fontanels - The anterior fontanel closes last at about 9-18 months - The posterior fontanel should close at 6-8 weeks
List all fine motor skills, gross motor skills, social and language for 1-12 months
Age Fine Motor Gross Motor Social/Language 0-3 months Fists clenched & Involuntary hand movements Hands in front of face and open
Lifts and turns head Head lag Rounded back Raises head and chest Improved head control Raises head in prone Slight head lag
Cooing Crying develops differentiation Smiling gurgling
4-6 months Bats at objects Grasps rattle Releases object to take another
Lifts head to look Rolls to back Head leads when pulled to sit Sits with back upright supported
Simple vowels Laughing & squealing Responds to voices Can distinguish emotion
7-9 months Transfers objects Pincer grasp Bangs objects together
Sits alone initially w/ support *by 8 without Crawls with abdomen off floor
Babbling Mamamama (strings) Responds to simple demands Peek-a-boo Stranger anxiety
10-12 months Fine pincer grasp Puts objects in & out of container Offers objects and releases them Feeds self with cup and spoon Simple paper marks Poking with index finger
Pulls to stand Cruising (walking while holding onto furniture) Sits from standing position *Walking independently
Mama & dada have meaning Mimicking sounds Recognizes objects by name Imitates animal sounds Separation anxiety
- Describe the following stages for 1-12 months
What is the Erikson Stage for Infants? Describe
What is the Piaget Stage for Infants? Describe
What is the type of play for infants? Appropriate toys? Trust vs. Mistrust Are needs met in a timely manner Do parents have best interest in mind
Sensorimotor stage Gathering information through senses Object permanence is not present
Solitary play Plastic containers of shapes Soft balls Wooden or plastic spoons Board books
- Stranger vs. Separation Anxiety- describe
Stranger anxiety develops around 8 months when they recognize that they are separate from their parents and become anxious when around those separate from their environment.
Separation anxiety develops in the last few moths of infancy and occurs when caretakers leave because they don’t understand that they will come back.
- Nutrition a. Breastfeeding/Bottle feeding - Breast feeding is encouraged but formula can also be used up to 6 months - 140-160ml/kg/day (newborn) - 105-108 kcal/kg/day (newborn)
b. Progression to solid foods - At 8 months ready for transition to solid foods - Start with veggies THEN fruit - Meats can be given at 10-12 months - Always make sure food is pureed or mashed
c. Juice/Milk/Transition to Sippy Cup - No fruit juice under 6 months (limited 2-4 ounces) - Offer a cup at 6-8 months
d. Foods to AVOID - Honey - Choking hazard foods (grapes, raw carrots, hot dogs) - Foods likely to cause an allergic reaction
- Anticipatory Guidance and Promoting Safety
a. Healthy Teeth and Gums - Washcloth to clean gums is fine - Once teeth develop use a soft bristle toothbrush - Erupt at 6 months; 4-8 teeth at a year (visit dentist) b. Injury prevention i. Home Safety - Due to sensorimotor stage choking is a common issue - Suffocation during sleeping is common so supine sleeping should be encouraged
ii. Car Seat Safety - Infants should always be in a rear facing car seat in the back seat
iii. Water Safety - Infants can drown in small amounts of water so make sure all areas with water are obstructed and locked - Water safety classes aren’t effective in preventing drowning as these skills may not be effective
c. Healthy Sleep and Rest - Newborns sleep most of the day 20 hours - At 3 months they should sleep 7-8 hours with a few naps - At 4 months sleep is more consistent and ability to self soothe - At a year they should sleep 8-12 hours with fewer naps - Always sleep on back with no items in crib (no co-sleeping)
Developmental Milestones
Language
2 months co
4 months haha
6 months babble
9 months mommy dada
12 months 1+ word
Gross motor
2 months raise head
4 months roll over
6 months sits up
9 months crawl
12 months walks
Social
2 months twinkles (smiles)
4 months focuses on sounds
6 months stranger anxiety
9 months name (responds)
12 months told commands (responds)
LOOK AT THE NUMBER
OF LETTERS IN EACH
MILESTONE!
2 months old raise your head
4 months old roll over fred
6 months sit up
9 months crawl
12 months walk and that’s all!
LOOK AT THE FIRST
LETTER OF EACH
MILESTONE!
Chapter 26: Growth and Development of the Toddler
Physical Growth a. Weight - 3-5 pounds per year - 4 times birthweight at 2 1/ b. Height - 3 inches per year c. Head circumference - 1 inch d. Fontanels - Anterior fontanel closed at 18 months
List all developmental skills for 12-36 months
Age Fine Motor Gross Motor Language/Sensory 12-15 months Build a tower of 2 cubes Walk without help Sensorimotor One word sentence (hungry, no, want) 18 months Build tower of 3-4 cubes Spoon use
Jump in place (both feet) Overhand ball throw
More than 50 words Two-to-three-word phrases Automatically says no 24 months Build a 6-7 cube tower Climb stairs Kick ball
36 months Build a tower of 8 cubes Draw a circle (circle-square-triangle)
- How can you promote healthy teeth and gums in the toddler?
2 years introduce toothpaste and fluoride either from water or toothpaste
Limit grazing; have more consistent meals
- Describe Toilet Training in a toddler? What are the signs of readiness? What is the order of gaining control over elimination?
Regular bowel movements, acknowledges need to use restroom
Bowel control - daytime bladder control – nighttime bladder control
- Developmental concerns:
a. Temper Tantrums: ignore as much as possible
b. Negativism: Avoid asking yes and no questions
c. Regression: if stressed they may regress; ignore regressive praise appropriate
- Injury Prevention: a. Motor Vehicle Injuries: make sure they aren’t around vehicles and make sure the straps go above the shoulders in car seat
b. Drowning: water safety courses can help but flotation devices and supervision are key
c. Burns: make sure hot or potentially hot items are out of reach and supervise if around stove, candle, etc.
d. Poisoning: keep dangerous items out of reach, do not refer to meds as candy
e. Choking and Suffocation: same foods that casue choking in infants should still be avoided whole grapes, hotdogs, etc.
f. Ingestion of Injurious Agents: keep batteries like small watch batteries out of reach and locked away
Chapter 27: Growth and Development of the Preschooler
List Physical Growth Changes: a. Proportional change: more slender, erect posture b. Weight gain: 5 pounds a year c. Height: 2-3 inches per year
List all developmental skills for 3-5 yo
Age Fine Motor Gross Motor Language/Sensory 3 yo Undresses self Holds a pencil
Climbs Pedals tricycle runs 4 yo Uses scissors Draws circles and squares Laces shoes
Throws ball overhand Kicks ball Hops on one foot
Asks questions Knows names of objects
5 yo Prints letters Dress and undress Uses utensils Ties shoes
Stands on one foot Swings and climbs Swimming and skating
Most speech is understood Name and address imagination
- Describe the following stages for the preschool age child.
What is the Erikson Stage for preschoolers? Describe
What is the Piaget Stage for preschoolers? Describe
What is the Kohlberg’s stage for preschoolers?
What is the common type of play for preschoolers? What is dramatic play? Initiative vs guilt
Inquisitive Feels sense of accomplishment when succeeding
Preoperational
Imaginative play Egocentric Lack of understanding of time
Preconventional
When punishment and rewards are established and there is more understanding
Associative play
Playing together and learning how to share, not much understanding of rules yet
- Please fill out the following table related to the expected nutrition of a preschooler
Promoting health eating habits
Picky eaters so parents should choose what they eat and the child can choose how much
Preventing overweight and obesity
Start healthy eating habits, limit juice intake, encourage physical play instead of tv or electronics
- How could you promote healthy sleep and rest in a preschooler?
Use night light, favorite toy, leave water by the bed, do not let them sleep with you
Having a routine is key
- How can you promote healthy teeth and gums in the preschooler?
Can brush own teeth but need supervision parents need to help floss
Go to the dentist 2 times a year
- How would you describe appropriate discipline to the parents of a preschooler?
Time out is very effective 1 minute per year also removal of privileges or toys is helpful
Chapter 28: Growth and Development of the School-age Child
Physical Growth a. Weight 7 pounds a year b. Height 2 inches a year c. Prepubescence 2 years before puberty,
List all developmental skills for 6-12 year olds
Age What activities promote fine motor development in the school-age child?
What activities promote gross motor development in the school-age child?
Language/Sensory Development
6-12 years Playing musical instruments
Riding a bike, skating, and swimming
Deeper understanding of language like metaphors and jokes Imitation of role models is common
- Describe the following stages for a 6-12 year old child.
What is the Erikson Stage for school-age child? Describe
What is the Piaget Stage for school-age child? Describe
What is the Kohlberg’s stage for school-age child?
What is the common type of play for school- age child? Industry vs. inferiority
Development of self worth and has satisfaction when developing a skill
Concrete operational
Understands principles of conservation (water test)
Postconventional
Develops own principles about contribution to the world Questioning of moral and religious values
Cooperative play
Organized sports Board games
- How could you promote healthy sleep and rest in a school age child?
10-12 hours is required from 6-12 but can vary, older children can have more variation on
weekends, naps are infrequent maybe one a day for energy boost
- How can you promote healthy teeth and gums in the school age child?
Should be brushing 2-3 times a day and have dental exams twice a year
Bruxism or teeth grinding may occur
- How can you promote learning in the school age child?
School attendance is important so there is emphasis on monitoring how they are doing and how
they are socializing with peers
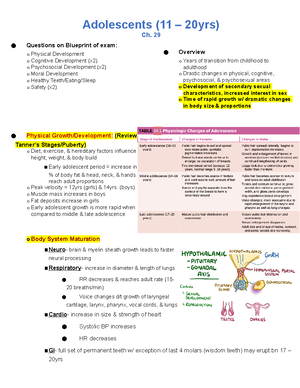
Chapter 29: Growth and Development of the Adolescent
Physical Growth a. Weight b. Height c. Puberty
Please fill in the following table about Tanner Staging:
Describe the following stages for a 13-18 year old child.
What is the Erikson
Stage for an
adolescent child?
Describe
What is the Piaget Stage for an adolescent child? Describe
What is the Kohlberg’s stage for an adolescent child?
How can we promote G&D through sports and physical fitness?
Identity vs role
confusion
Development of sense
of self
Formal operational
Logical and organized thinking
Post conventional
Development of one’s own values and morals
Infant/Newborn Assessment - Newborn screening tests for 45 genetic disorders and should be obtained 24-48 hours after birth and at 2-week checkup.
Infant Physical Development - It is normal to lose 10% of body weight within first week Should regain birthweight by 10-14 days /Birthweight should double by 4 months and triple by 1 year/ Height should increase by 50% in 1 year A 10 cm gain in a year is normal/ posterior closes first anterior last
Infant Cognitive Development – sensorimotor stage
Infant Psychosocial Development – page 7
Infant Psychosocial Development – page 7
Infant Gross/Fine Motor Skills – page 7
Infant Gross/Fine Motor Skills – page 7
Infant Healthy Teeth/Eating/Sleep/Discipline
Infant Safety
Toddler Growth
Toddler Cognitive Development
Toddler Psychosocial Development
Toddler Language
Toddler Gross/Fine Motor Skills
Toddler Healthy Teeth/Eating/Sleep/Discipline
Toddler Healthy Teeth/Eating/Sleep/Discipline
Toddler Safety
Toddler Safety
Preschool Physical Development
Preschool Cognitive Development
Preschool Psychosocial Development
Preschool Moral Development
Preschool Gross/Fine Motor Skills
Preschool Healthy Teeth/Eating/Sleep
Preschool Safety
Preschool Safety
School Physical Development
School Cognitive Development
School Cognitive Development
School Psychosocial Development
School Moral Development
School Gross/Fine Motor Skills
School Healthy Teeth/Eating/Sleep
School Safety
Adolescent Physical Development
Adolescent Cognitive Development
Adolescent Cognitive Development
Adolescent Psychosocial Development
Adolescent Psychosocial Development
Adolescent Moral Development
Adolescent Healthy Teeth/Eating/Sleep
Adolescent Safety
Adolescent Safety
Immunization types/schedule – can’t receive a live attenuated until 1 year
Vaccine-preventable diseases
Vaccine-preventable diseases
Vaccine-preventable diseases
Administering immunizations
Overcoming barriers- Immunization – central records, combo vaccines
Vaccine Contraindications and Precautions – ONLY PERMENANT CONTAINDICATION IS ANAPHYLAXIS/ increased risk of adverse reaction is precaution
Diphtheria - tonsils AIRWAY OBSTRUCTION
Pertussis – whooping cough
Tetanus – neurological fatal
Hemophilus influenza – causes life threatening infections (meningitis)
Polio – permanent paralysis
Measles – airborne precautions/ kolpik spots/ rash
Mumps – neck swelling/ droplet
Rubella – droplet
Hep A – contaminated food & drinking water
Hep B – mother to newborn
Varicella – airborne/contact precautions
Pneumococcus – pneumonia/sepsis
Rotavirus – watery diarrhea. Contraindicated w/ intestine folding
HPV – sexual contact
Meningococcal – college = high risk/ meningitis
PEDS EXAM 1 Study Guide
Course: Pediatric Nursing Care (MCN 354)
University: University of South Alabama

- Discover more from: