- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Immune System Drugs - Dfgghh
Course: Nursing Fundamentals (Nurs 100)
999+ Documents
Students shared 1137 documents in this course
University: West Coast University
Was this document helpful?

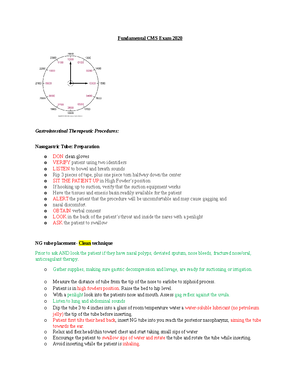
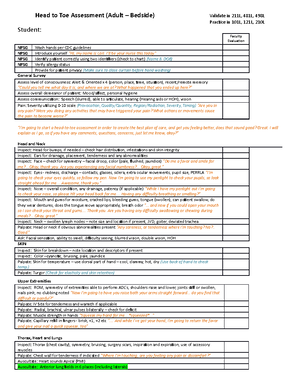
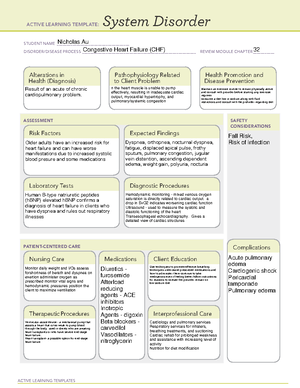
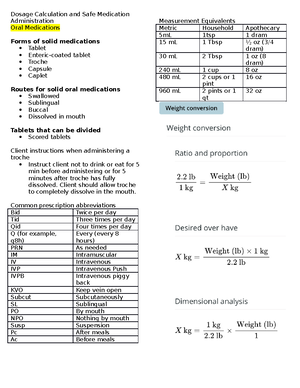
28-1 IMMUNOLOGIC AGENTS: VACCINES & TOXOIDS
WHAT DO THEY DO?
The weakened or killed antigens contained
in the vaccine do not have sufficient strength
to cause disease. Although it is a rare
occurrence, vaccination with any vaccine
may not result in a protective antibody
response in all individuals given the vaccine.
A toxin that is attenuated (or weakened) but
still capable of stimulating the formation of
antitoxins is called a toxoid .
INDICATIONS
❖Routine immunization of infants and
children
❖Immunization of adults against
tetanus
❖Immunization of adults at high risk
for certain diseases (e.g.,
pneumococcal and influenza
vaccines)
❖Immunization of children or adults at
risk for exposure to a particular
disease (e.g., hepatitis A for those
going to endemic areas)
❖Immunization of prepubertal girls or
nonpregnant women of childbearing
age against rubella
ADVERSE REACTIONS
❖Chills, fever
❖muscular aches and pains
❖Rash
❖ lethargy
CONTRAINDICATIONS
❖Immunologic agents are contraindicated in patients with
known hypersensitivity to the agent or any component of
it. Allergy to eggs is a concern with some vaccines.
❖The measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella vaccines are
contraindicated in patients who have had an allergic
reaction to gelatin, neomycin, or a previous dose of one of
the vaccines
❖ Vaccines and toxoids are contraindicated during acute
febrile illnesses, leukemia, lymphoma,
immunosuppressive illness or drug therapy, and non
localized cancer. Always ask about allergy history before
preparing a vaccine for administration
INTERACTIONS
Vaccinations containing live organisms are
not administered within 3 months of
immune globulin administration, because
antibodies in the globulin preparation may
interfere with the immune response to the
vaccination. Corticosteroids, antineoplastic
drugs, and radiation therapy depress the
immune system to such a degree that
insufficient numbers of antibodies are
produced to prevent the disease. When the
salicylates are administered with the
varicella vaccination, there is an increased
risk of Reye’s syndrome developing.
NURSING MANAGEMENT
❖Most vaccine preparations require refrigeration.
Always have a backup plan for storage of the
vaccine should the health care facility lose
power. Temperature fluctuations can harm the
vaccines.
❖Monitor the patient before allowing them to
leave after administering any vaccine.
❖State agencies, drug companies, and
immunization organizations all provide
standardized forms for parents or caregivers
that document immunization history. In
addition to your facility documentation,
provide or record on the document presented
by the parent or caregiver the following
information:
❖ Date of vaccination
❖ Route and site, vaccine type, manufacturer
❖ Lot number and expiration date
❖ Name, address, and title of individual
administering vaccine
❖