- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Paediatric ENT Summary
Course: Medicine (MBCH11002)
185 Documents
Students shared 185 documents in this course
University: The University of Edinburgh
Was this document helpful?

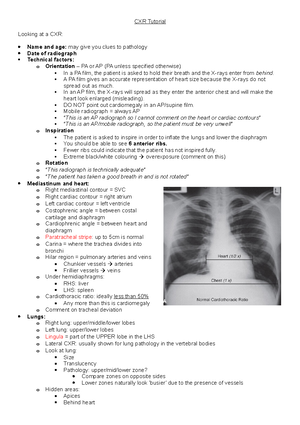
ENT Hx and Exam
Sore Throat
Viral more common
S. pyogenes:
oSpots of white
oRx:
Penicillin V (NOT amoxicillin, as if EBV full-body rash)
Painkillers
If can’t swallow, IV fluids
EBV:
oCarpet of white
oRed petichiae on soft palate
oUsually the cause if airway obstruction
oHepatosplenomegaly:
Take LFTs
Beware alcohol, contact sport
Tonsillectomy indications:
o3/yr for 3 yrs
o5/yr for 2 yrs
o7/yr for 1 yr
oObstructive sleep apnoea
oMalignancy
oBad halitosis
Tonsillectomy complications:
oWorsening pain in throat
oBleeding::
W/in 24 hours = primary
Later = secondary (probably infection)
1 in 100 back to theatre due to bleeding
Adenoids
Symptoms:
oOSA
oMouth-breathing
oNasal discharge, PND
Can get desaturation after removal due to increased O2 w/ hypoxic drive
Acute Otitis Media
Often caused by common cold, congested pharynx blocked Eustachian
tube
Child Eustachian tube:
Students also viewed
Related documents
- BMS3b Respiration - Physiology and Biochemistry
- HS5 Health Promotion - Summary Medicine
- Neuroanatomy 3 - Descending (Motor) Pathways
- GI & Liver Anatomy 4 - Abdominal Viscera (not gut tube)
- GI & Liver Anatomy 2 - Peritoneum Within the Fully Developed Abdominal Cavity
- GI & Liver Anatomy 1 - Anterior Abdominal Wall