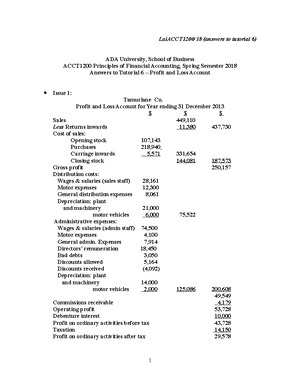
- Information
- AI Chat
Income Taxation - Cpar test bank
Marketing (2502)
Adamson University
Comments
- Thank you so much
- This power is superior to the non-impairment clause and is broader in application because it is a power to make and implement the laws.
- i love this!!! :))
- thank you
- Thank you for uploading this! It is a really great help :)
Students also viewed
Related documents
- Solution-set-n compress
- 32 Share Based Payment - This will help a lot aboit marketimg course, beacuse it contsins lectures that
- Math10-Q4-W5 - This will help a lot aboit marketimg course, beacuse it contsins lectures that
- Dokumen - This will help a lot aboit marketimg course, beacuse it contsins lectures that
- accounting101reviewer
- Phototropism key points
Preview text
TAXATION 1 – Income Taxation
General Principles of Taxation
Taxation as distinguished from police power and power of eminent domain. A. Property is taken to promote the general welfare. B. Maybe exercised only by the government. C. Operates upon the whole citizenry. D. There is generally no limit as to the amount that may be imposed.
The following are constitutional limitations, except A. No imprisonment for non-payment of poll tax. B. Non-impairment of the obligation of contracts. C. Rule of uniformity and equity in taxation. D. Exemption from income tax of charitable institutions, cemeteries, churches, personage or convents appurtenant thereto, as well as all lands, buildings and improvements actually, directly and exclusively used for religious, charitable and educational purposes.
Which of the following statements is correct? A. The President is authorized to increase or decrease national internal revenue tax rates. B. One of the nature of taxation is the reciprocal duties of protection and support between the state and subjects thereof. C. Every sovereign government has the inherent power to tax. D. Income tax in an indirect tax.
A tax must be imposed for public purpose. Which of the following is not a public purpose? A. National defense B. Public education C. Improvement of the sugar and coconut industries. D. Improvement of a subdivision road.
Which is not an essential characteristic of a tax? A. It is unlimited as to amount. B. It is payable in money. C. It is proportionate in character. D. It is an enforced contribution.
Special assessment is an enforced proportional contribution from owners of land especially benefited by public improvement. Which one of the following is not considered as one of its characteristics? A. It is levied on land. B. It is based on the government’s need of money to support its legitimate objectives. C. It is not a personal liability of the persons assessed. D. It is based solely on the benefit derived by the owners of the land.
It is the privilege of not being imposed a financial obligation to which others are subject. A. Tax incentive B. Tax exemption C. Tax amnesty D. Tax credit
As to scope of the legislative power to tax, which is not correct? A. Where there are no constitutional restrictions, and provided the subjects are within the territorial jurisdiction of the state, Congress has unlimited discretion as to the persons, property or occupations to be taxed.
B. In the absence of any constitutional prohibition, Congress has the right to levy a tax of any amount it sees fit. C. The discretion of Congress in imposing taxes extends to the mode, method or kind of tax, unless restricted by the constitution. D. The sole arbiter of the purpose or which taxes shall be levied is Congress, provided the purpose is public and the courts may not review the levy of the tax to determine whether or not the purpose is public.
Which of the following is a nature of taxation? A. The power is granted by legislative action. B. It is essentially an administrative function. C. It is generally payable in money. D. Without it the state can continue to exist.
Which of the following is not a determinant of the place of taxation? A. Source of the income B. Citizenship of the taxpayer C. Residence of the taxpayer D. Amount of tax to be imposed
Which of the following statements is not correct? A. An inherent limitation of taxation may be disregarded by the application of a constitutional limitation. B. The property of an educational institution operated by a religious order is exempt from property tax, but its income is subject to income tax. C. The prohibition of delegation by the state of the power of taxation will still allow the BIR to modify the rules in time for filing of returns and payment of taxes. D. The power of taxation is shared by the legislative and executive departments of the government.
Statement 1 – The point on which tax is originally imposed is impact of taxation. Statement 2 – Eminent domain is inferior to non-impairment clause of the constitution. Statement 3 – As a rule, taxes are subject to set-off or compensation. Statement 4 – As a rule, provisions on the validity of tax exemptions are resolved liberally in favor of the taxpayer.
Statement 1Statement 2Statement 3Statement 4 A. True False False True B. False True True False C. True True False False D. False False True True
A tax system where the revenues are supplied mostly by indirect taxes. A. Schedular C. Progressive B. Proportional D. Regressive
A tax system where the greater bulk of the tax revenues is derived by direct taxes. A. Schedular C. Progressive B. Proportional D. Regressive
This is an inherent limitation on the power of taxation. A. Rule on uniformity and equity in taxation. B. Due process of law and equal protection of the laws. C. Non-impairment of the jurisdiction of the Supreme Court in tax cases. D. Tax must be for the public purpose.
B. Situs of taxation D. Theory of taxation
The existence of the government is a necessity and that the state has the right to compel all individuals and property within its limits to contribute A. Basis of taxation C. Scope of taxation B. Situs of taxation D. Theory of taxation
The reciprocal duties of support and protection between the people and the government. A. Basis of taxation C. Scope of taxation B. Situs of taxation D. Theory of taxation
Subject to inherent and constitutional limitations, the power of taxation is regarded as supreme, plenary, unlimited and comprehensive. A. Basis of taxation C. Scope of taxation B. Situs of taxation D. Theory of taxation
Our National Internal Revenue Laws are A. Political in nature C. Criminal in nature B. Penal in nature D. Civil in nature
The levying or imposition of tax and the collection of the tax are processes which constitute the taxation system. A. Basis of taxation C. Nature of taxation B. Aspects of taxation D. Theory of taxation
The process or means by which the sovereign, through its law-making body raises income to defray the expenses of the government. A. Toll C. Taxation B. License fee D. Assessment
Enforced proportional contributions from persons and property levied by the state by virtue of its sovereignty for the support of the government and for all public needs. A. Toll C. Taxes B. License fee D. Assessment
An escape from taxation where the tax burden is transferred by the one on whom the tax is imposed or assessed to another. A. Shifting C. Transformation B. Exemption D. Capitalization
An escape from taxation where the producer or manufacturer pays the tax and endeavors to recoup himself by improving his process of production thereby turning out his units of products at a lower cost. A. Shifting C. Transformation B. Exemption D. Capitalization
An escape from taxation where there is a reduction in the price of the taxed object equal to the capitalized value of future taxes which the taxpayer expects to be called upon to pay. A. Shifting C. Transformation B. Exemption D. Capitalization
The use of illegal or fraudulent means to avoid or defeat the payment of tax. A. Exemption C. Avoidance B. Shifting D. Evasion
The use of legal or permissible means to minimize or avoid taxes. A. Exemption C. Avoidance
B. Shifting D. Evasion
Synonymous to tax evasion. A. Tax dodging C. Tax exemption B. Tax minimization D. Tax evasion
Synonymous to tax avoidance. A. Tax dodging C. Tax exemption B. Tax minimization D. Tax evasion
In every case of doubt, tax statutes are construed A. Strictly against the government and the taxpayer. B. Liberally in favor of the government and the taxpayer. C. Strictly against the government and liberally in favor of the taxpayer. D. Liberally in favor of the government and strictly against the taxpayer.
In every case of doubt, tax exemptions are construed A. Strictly against the government and the taxpayer. B. Liberally in favor of the government and the taxpayer. C. Strictly against the government and liberally in favor of the taxpayer. D. Liberally in favor of the government and strictly against the taxpayer.
In case of conflict between the Tax Code and the Philippine Accounting Standards (PAS). A. PAS shall prevail over the Tax Code. B. Tax Code shall prevail over PAS. C. PAS and Tax Code shall be both disregarded. D. The taxpayer may choose between the PAS or the Tax Code. .
Tax of a fixed amount imposed upon all persons residing within a specified territory without regard to their property or occupation they may be engaged. A. Personal, poll or capitation C. Excise B. Property D. Regressive
Tax imposed on personal or real property in proportion to its value or on some other reasonable method of apportionment. A. Personal, poll or capitation C. Excise B. Property D. Regressive
Tax imposed upon performance of an act, the enjoyment of privilege or the engaging in an occupation. A. Personal, poll or capitation C. Excise B. Property D. Regressive
Tax which is demanded from the person whom the law intends or desires to pay it. A. Direct C. Excise B. Indirect D. Percentage
Tax which is demanded from one person in the expectation and intention that he shall indemnify himself at the expense of another. A. Direct C. Excise B. Indirect D. Percentage
Tax which imposes a specific sum by the head or number or by some standard of weight or measurement and which requires no assessment other than a listing or classification of the objects to be taxed. A. Specific C. Excise B. Ad-valorem D. Income
The distinction of a tax from permit or license fee is that a tax is: A. Imposed for regulation. B. One which involves an exercise of police power. C. One in which there is generally no limit on the amount that maybe imposed. D. Limited to the cost of regulation.
Police power as distinguished from the power of eminent domain: A. Just compensation is received by the owner of the property. B. Maybe exercised by private individuals. C. May regulate both liberty and property. D. Property is taken by the government for public purpose.
A tax wherein both the incidence of or the liability for the payment of the tax as well as the burden of the tax falls on the same person. A. Direct tax C. Indirect tax B. Value added tax D. Percentage tax
Which one of the following is not a characteristic or element of a tax? A. It is an enforced contribution. B. It is legislative in character. C. It is based on the ability to pay. D. It is payable in money or in kind.
Tax as distinguished from license fees: A. Limited to cover cost of regulation. B. A regulatory measure. C. Non-payment does not necessarily render the business illegal. D. Imposed in the exercise of police power.
The power of taxation is exercised by A. The President C. Bureau of Internal Revenue B. The Supreme Court D. Congress
One of the characteristics of internal revenue laws is that they are: A. Criminal in nature C. Political in nature B. Penal in nature D. Generally prospective in application.
Which of the following is not an example of excise tax: A. Transfer tax C. Real property tax B. Sales tax D. Income tax
The following are similarities of the inherent power of taxation, eminent domain, and police power, except one: A. Are necessary attributes of sovereignty B. Superior to the non-impairment clause of the constitution. C. Compensation is received. D. Are legislative in character.
Which of the following is not a scheme of shifting the incidence of taxation? A. The manufacturer transfers the tax to the consumer by adding the tax to the selling price of the goods sold; B. The purchaser asks for a discount or refuse to buy at regular prices unless it is reduced by the amount equal to the tax he will pay; C. Changing the terms of the sale like FOB shipping point in the Philippines to FOB destination abroad, so that the title passes abroad instead of in the Philippines; D. The manufacturer transfers the sales tax to the distributor, then in turn to the wholesaler, in turn to the retailer and finally to the consumer.
Which of the following statements is not correct? A. Taxes may be imposed to raise revenues or to provide disincentives to certain activities within the state; B. The state can have the power of taxation even if the Constitution does not expressly give it the power to tax. C. For the exercise of the power of taxation, the state can tax anything at any time. D. The provisions of taxation in the Philippine Constitution are grants of power and not limitations on taxing powers.
License fee as distinguished from tax: A. Non-payment does not necessary render the business illegal. B. A revenue raising measure C. Imposed in the exercise of taxing power. D. Limited to cover cost of regulation.
Value-added tax is an example of: A. Graduated tax C. Regressive tax B. Progressive tax D. Proportional tax
Which tax principle is described in the statement “ the more income earned by the taxpayer, the more tax he has to pay.” A. Fiscal Adequacy C. Administrative feasibility B. Theoretical justice D. Inherent in sovereignty
The most superior and least limitable among the fundamental powers of the state: A. Power of recall C. Power of taxation B. Police power D. Power of eminent domain
One of the characteristics of a tax is that: A. It is generally based on contact. B. It is generally payable in money. C. It is generally assignable. D. It is generally subject to compensation.
The following are the characteristics of our internal revenue laws except: A. Political in nature. B. Civil in nature. C. Generally prospective in application. D. May operate retrospectively if congress so provides.
Which of the following has no power of taxation? A. Provinces C. Barangays B. Cities D. Barrios
Which of the following statements is wrong? A revenue bill: A. Must originate from the House of Representatives and on which same bill the Senate may propose amendments. B. May originate from the Senate and on which same bill the House of Representatives may propose amendments. C. may have a House version and a Senate version approved separately, and then consolidated, with both houses approving the consolidation version. D. May be recommended by the President to Congress.
Tax as distinguished from special assessment:
Tax as distinguished from debt A. no imprisonment for non-payment C. based on contract B. may be paid in kind D. based on law
Congress can impose a tax at any amount and at anytime shows that A. Taxation is an inherent power of the state. B. Taxation is essentially a legislative power. C. Taxation is a very broad power of the state. D. Taxation is based on taxpayers’ ability to pay.
The amount required is dictated by the needs of the government in: A. License fee C. Toll B. Tax D. Debts
A charge imposed on land for special benefits derived resulting from public improvements. A. Tax C. License B. Toll D. Special assessment
Which of the following are National Internal Revenue Taxes? I. Income tax III. Donor’s tax V. Other percentage tax II. Estate tax IV. Value Added tax VI. Excise Tax VII. Documentary stamp tax
A. I, II, III, IV C. I, II, III, IV, V, VI B. I, II, III, IV, V D. I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII
The Bureau of Internal Revenue shall have a chief and four (4) assistant chiefs to be known as A. Secretary and Assistant Secretaries B. Secretary and Undersecretaries C. Commissioner and Assistant Commissioners D. Commissioners and Deputy Commissioners
The three fundamental powers of the state are I. Inherent in the state and may be exercised by the state without need of any constitutional grant. II. Not only necessary but indispensable.
A. True; True C. False; true B. True; false D. False; false
- The three fundamental powers of the state are I. Methods by which the state interfere with private rights. II Exercised primarily by the legislature.
A. True; True C. False; true B. True; false D. False; false
I. Police power regulates both liberty and property while the power of eminent domain and the power of taxation affect only property rights. II Police power and the power of taxation may be exercised only by the government while the power of eminent domain may be exercised by some private entities. A. True; True C. False; true B. True; false D. False; false
I. The property taken in police power is destroyed while the property taken under the power of eminent domain and power of taxation are not destroyed. II. In power of taxation, the compensation received is the protection afforded to the citizens; in police power the compensation received is the altruistic feeling that somehow you contributed to the promotion of the general welfare; in power of eminent domain, the compensation received is the just compensation paid for the property taken.
A. True; True C. False; true B. True; false D. False; false
- I. The point on which a tax is originally imposed is impact of taxation. II. The point on which a tax burden finally rests or settles down is incidence of taxation.
A. True; True C. False; true B. True; false D. False; false
- I. Police power is superior to the non-impairment clause of the constitution. II. Power of taxation is superior to the non-impairment clause of the constitution.
A. True; True C. False; true B. True; false D. False; false
- I. No person shall be imprisoned for debt or non-payment of tax. II. Tax laws are civil and penal in nature because there are penalties provided in case of violation.
A. True; True C. False; true B. True; false D. False; false
- I. Tax may be collected in an unlimited amount. II. License fee may be collected in an unlimited amount.
A. True; True C. False; true B. True; false D. False; false
I. Tax is imposed to raise revenue. II. License fee is imposed to raise revenue. A. True; True C. False; true B. True; false D. False; false
I. Tax is a demand of sovereignty. II. Toll is a demand of sovereignty.
A. True; True C. False; true B. True; false D. False; false
- I Tax is imposed on persons, property, and property rights. II. Special assessment is imposed on persons, property, and property rights.
A. True; True C. False; true B. True; false D. False; false
- I. Collection of tax is a legislative act. II. Imposition of tax is an administrative act.
A. True; True C. False; true B. True; false D. False; false
- I. The President has the power to veto a revenue bill even if such bill was already approved by Congress. II. The President is superior to Congress as he/she can veto any bill even if already approved by Congress.
A. True; True C. False; true B. True; false D. False; false
INDIVIDUAL TAXPAYERS
The National Internal Revenue Code of 1988 is A. RA 9337 B. CA 466 C. RA 9504 D. RA 8424
Which of the following statements is not correct? A. An individual citizens of the Philippines who is working and deriving income from abroad as an overseas contract worker is taxable on income from sources within and without the Philippines. B. A seaman who is a citizen of the Philippines and who receives compensation for services rendered abroad as a member of the complement of vessel engaged exclusively in international trade shall be treated as a resident citizen. C. A non- resident citizen who is not engaged in business in the Philippines is treated as non-resident alien who is not engaged in business in the Philippines D. An alien individual, whether a resident or not of the Philippines, is taxable only on income derived from sources in the Philippines
Which of the following statements is not correct? A. In the case of married individuals, where only one of the spouses is deriving gross income, only such spouse shall be allowed the personal exemption. B In the case of married individuals, the additional exemptions maybe claimed by only one of the spouses C. As a rule, the husband shall be the head of the family and proper claimant of the additional exemption D. In the case of legally separated spouses, additional exemption maybe claimed by the spouses who has custody of the children but shall not exceed four(4) for each spouse
A resident citizen is taxable on all income derived from sources A. Within the Philippines only B. Without the Philippines only C. Partly within and partly without D. Within and without the Philippines
A non-resident citizen is taxable on all income derived from sources A. Within the Philippines only B. Without the Philippines only C. Partly within and partly without D. Within and without the Philippines
A resident alien is taxable on all income derived from sources
A. Within the Philippines only B. Without the Philippines only C. Partly within and partly without D. Within and without the Philippines
A non-resident alien is taxable on all income derived from sources A. Within the Philippines only B. Without the Philippines only C. Partly within and partly without D. Within and without the Philippines
The following taxpayers are allowed to claim additional exemptions, except A. Resident citizens B. non- resident citizens C. Resident aliens D. Non-resident aliens
Which of the following statements is not correct? A. If only one spouse is deriving taxable income, only said spouse may claim the additional exemption B. If both spouses earn taxable income only one of the spouses can claim additional exemption C. If legally separated from the spouse, the husband can claim the additional exemption unless he waives the right in favor of his wife D. An unmarried individual with a child out of wedlock can claim a personal exemption as a head of the family plus exemption
10 citizen of the Phils. who works and derives income from abroad is a resident if he stayed outside the Phils. A. For less than 180 days B. For more than 180 days C. For 183 days or more D. For less 183 days
A citizen of the Phils. Who works abroad and whose employment requires him to be physically present abroad most of the time during taxable years A. Taxable on income within and without the Phils. B. Taxable on income from without the Phils. C. Exempt from income tax D. Taxable income from within the Phils.
A citizen of a foreign country is considered a non-resident alien engaged in business in the Phils. If he stayed inside the Phils. A. For 183 days or more B. For less than 183 days C. For more than 180 days D. For less than 180 days
Which of the following dependents is not qualified to entitle a taxpayer additional persona exemption? A. Recognized natural son who celebrated his 21st birthday during the taxable year. B. Legitimate natural son, 21 years old who got married on December 31, of the year. C. Legally adopted son, 21 years old son who became employed December 30, of the taxable year.
The total basic personal and additional exemption in 2009 is: A, 000 B. P100, 000 C. P125, 000 D. P75, 000
A married, earned P225, 000 (net of P40, 000 w/tax) compensation income from employment from July to December 2010. He has a legally adopted child as qualified dependent and paid P3,000 as health and hospitalization insurance premiums. For 2010, he can deduct premiums for health and hospitalization insurance of: A. P3, 000 B. P2, 400 C. P1, 200 D. P
Using the preceding number, his personal and additional exemption is A. P40, 000 B. P75, 000 C. P77,400 D. P78,
Which of the following individual taxpayers cannot avail of the allowed deductions for health and hospitalization insurance premiums? A. Non-Resident citizen B. Resident alien C. Non-resident alien engaged in business in the Phil. D. Non-resident alien not engaged in business in the Phil.
Taxable on income from all sources within and without the Phil. A. Resident citizenB. Non-resident citizen C. Resident alien D. Non-resident alien
Taxable only on income from sources within the Phil. except A. Resident citizenB. Non-resident citizen C. Resident alien D. Non-resident alien
May not claim personal exemption A. Non-resident citizen B. Non-resident alien engaged in trade or business in the Phil. Under certain conditions C. Resident alien D. Non-resident alien who stayed in the Phil. For 175 days
Exemption which is determined according to the status of the taxpayer A. Personal exemption B. Additional Exemption C. Optional standard deduction D. Special additional personal exemption
Exemptions allowed based on presence of qualified dependent children A. Personal exemption B. Additional Exemption C. Optional standard deduction D. Special additional personal exemption
Will not qualify as dependent A. Legitimate child B. Brother C. Mother D. Nephew
Personal exemption, if single A. P20, 000 B. P25, 000 C. P32, 000 D. P50, 000
Personal exemption, if married but judicially declared as legally separated with no dependent. A. P20, 000 B. P25, 000 C. P32, 000 D. P50, 000
Personal exemption, if married but living separately without judicial decree of separation
A. P20, 000 B. P25, 000 C. P32, 000 D. P50, 000
Personal exemption, if married but judicially declared as legally separated with dependent A. P20, 000 B. P25, 000 C. P32, 000 D. P50, 000
Personal exemption, if head of the family A. P20, 000 B. P25, 000 C. P32, 000 D. P50, 000
Amount of additional exemption each qualified dependent child is A. P8, 000 B. P100, 000 C. P50, 000 D. P25, 000
The number of dependent children who will qualify for additional exemption purposes shall not exceed. A. 3 children B. 4 children C. 5 children D. 6 children
An unmarried or legally separated man or woman with one or both parents, or with one more brothers and sisters, or with one or more legitimate, illegitimate, or legally adopted children living with and dependent upon him or her for their chief support, where such brothers, or sisters, or children, regardless of age are incapable of self-support because of mental physical defect.
A. Good father of a family B. Married C. Single D. Head of the family
A non-resident alien is deemed doing business in the Phil. If he A. Is an individual whose residence is within the Phil. B. Is an individual whose father or mother is an alien who is engaged in business in the Phil. C. Is an individual who is naturalized in accordance with law D. Shall come to the Phil. And stay therein for an aggregate period of more than 180 days during a calendar year.
One is not correct A. If the taxpayer marries during the taxable year, he may claim the personal exemption in full as a married person for such year. B. If the taxpayer dies during the taxable year, his estate may still claim the personal and additional exemption for himself and his dependents as if he died at the close of such year. C. If the spouse of the taxpayer or any of the dependents dies during the taxable year, the taxpayer may still claim the same exemptions as if death occurred at the close of such year. D. If the taxpayer should have additional dependent children during the taxable year, he can always claim the additional exemptions for such year.
One is correct A. Where both husband and wife receive compensation income, the additional exemption shall be claimed by wife unless she explicitly waives her right in favor of her husband in the withholding exemption certificate. B. Husband and wife shall be treated as separate taxable units and each shall be allowed to claim personal exemption C. If the gross income does not exceed P20, 000, a special additional personal exemption of P4, 000 may be claimed by the taxpayer. D. Husband and wife shall be treated as separate taxable units and shall be allowed to claim only one personal exemption either for the husband or wife at their option.
A. The term “chief support” means more than one-half of the requirements for support B. If two children contribute equal amounts for the support of dependent, neither one of them may be qualify as head of the family
If the taxpayer is non-resident alien not engaged in business in the Phil. married and his country grants P35, 000 as personal exemption for married individuals, his taxable income is? A. P370, 000 B. P170, 000 C. P200, 000 D. P400, 000
With regard to deduction for premiums on hospitalization and health insurance, which of the following statements is wrong? A. Allowed as deduction even if income is from compensation only B. Allowed as deduction even if income is from business or practice of Profession C. Allowed as deduction even if mixed income D. Allowed as deduction only if the taxpayer is taking itemized deductions from gross income.
Which of the following statements is wrong? The premiums on hospitalization and health insurance may be deducted A. Not exceed P2, 400 a year per family B. Not exceed P200 per month C. If the family income doesn’t exceed P250, 000 D. By either spouse in the case of married individuals
A resident, single with qualified dependent illegitimate children had the following during the calendar year. Gross compensation income P250, 000 Expenses related to his employment 120, 000 SSS premium contributions 3, 600 Philhealth contribution 2, 400 Pag-ibig contributions 2, 000 Union dues 1, 000 Premiums on health insurance 4, 000 The taxable income before personal and additional exemption is A. P237, 000 B. P241, 000 C. P238, 600(?) D. P117, 000
In which of the following should additional exemption not be allowed to the taxpayer? A. An alien, whose dependent child is living with him in the Phil. B. A resident citizen, who has 25 years old mentally retarded son C. A resident citizen, who has a 50 years old mother as his dependent D. a resident alien with an illegitimate child, 7 years old . CORPORATION
For income taxation purposes, the term “corporation ” excludes one of the following : A. Ordinary partnership B. An incorporated business organization C. General professional partnership D. Business partnership
Which of the following is subject to the corporate income tax? A. a non- stock and non profit educational institution B. Public educational institution C. Private cemeteries D. Civic league or organization not organized for profit and operated exclusively for the promotion of social welfare
A corporation organized and created under the laws of a foreign country and is authorized to do business/ trade in the Phil. is: A. Domestic corporation C. Non-resident foreign corporation B. Resident foreign corporation D. General co-partnership
One of the general principles of income taxation: A. A foreign corporation engaged in business in the Phil. is taxable on all income derived from sources within and without the Phil. B. A foreign corporation engaged in business in the Phil. is taxable on all income derived from sources within the Phil. only. C. A domestic corporation is taxable on income derived from sources within the Phil. only. D. A domestic corporation is taxable on income derived from sources without the Phil. only.
One of the following doesn’t fall under the definition of a “corporation” for income tax purpose: A. General partnership B. Joint stock company C. Insurance company D. Sole partnership
Which of the following is classified as Special Corporation subject to preferential corporate income tax rate? A. Social security System C. Phil. Charity Sweepstakes Office B. Proprietary Educational Institution D. Government Service Insurance System
A corporation which may be classified as either a resident corporation or non-resident Corporation is A. Domestic corporation C. Government owned and controlled corporation B. Foreign corporation D. Non-profit hospital
The Phil. Health Insurance Corporation, a government owned corporation is: A. Exempt from the corporate income tax B. Subject to the preferential corporate income tax for special corporations. C. Subject to the basic corporate income tax. D. Subject to final tax.
Public educational institutions, like the University of the Philippines is deemed by law: A. subject to preferential corporate income tax for special corporations. B. Subject to the basic corporate income tax C. Subject to both the preferential income tax and the basic corporate income tax. D. Exempt from the corporate income tax.
Which is not correct? The following are exempt from the corporate income tax: A. Philippine Charity Sweepstakes Office C. Gov’t. owned or controlled corp. B. Bureau of Internal Revenue D. Social Security System
Which of the following maybe subject to the corporate income tax? A. A non-profit educational institution C. A private educational Institution B. A public educational Institution D. Government Service Insurance System
A domestic corporation may employ, as a basis for filing its annual corporate return the: A. Calendar year only C. Either calendar or fiscal year B. Fiscal year only D. Neither calendar nor fiscal year
A corporation files a quarterly return within A. 30 days after the end of each of the 3 quarters B. 60 days after the end of each of the first 3 quarters C. 30 days after the end of each of the first 4 quarters D. 60 days after the end of each of the first quarters
A final or annual return is filed on or before the 15th day of the?
Income Taxation - Cpar test bank
Course: Marketing (2502)
University: Adamson University

- Discover more from:
Students also viewed
Related documents
- Solution-set-n compress
- 32 Share Based Payment - This will help a lot aboit marketimg course, beacuse it contsins lectures that
- Math10-Q4-W5 - This will help a lot aboit marketimg course, beacuse it contsins lectures that
- Dokumen - This will help a lot aboit marketimg course, beacuse it contsins lectures that
- accounting101reviewer
- Phototropism key points