- Information
- AI Chat
Was this document helpful?
Ibuprofen - Medication
Course: Nursing Pharmacology
587 Documents
Students shared 587 documents in this course
University: Keiser University
Was this document helpful?

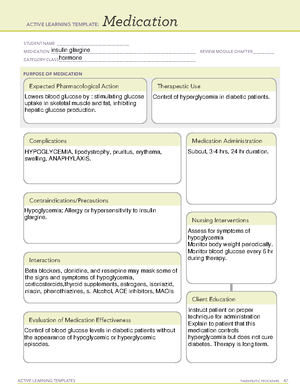
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES THERAPEUTIC PROCEDURE A7
Medication
STUDENT NAME _____________________________________
MEDICATION __________________________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER ___________
CATEGORY CLASS ______________________________________________________________________
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE:
PURPOSE OF MEDICATION
Expected Pharmacological Action
Complications
Contraindications/Precautions
Interactions
Medication Administration
Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness
Therapeutic Use
Nursing Interventions
Client Education
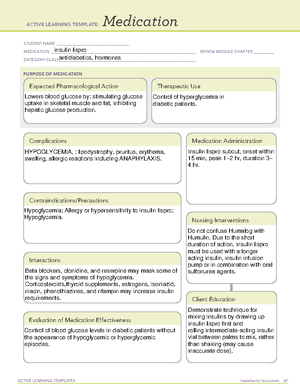
Ibuprofen
Antipyretics, antirheumatics, nonopioid analgesics
Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis.
PO adults: anti-inflammatory,
analgesic, antidysmenorrheal,
antipyretic.
PO children (6 mo- 12yr):
Anti-inflammatory, antipyretic,
cystic fibrosis.
PO (infants and children):
analgesic.
May limit the cardioprotective effects of low-dose aspirin.
Concurrent use with aspirin maypeffectiveness of
ibuprofen. Additive adverse GI side effects with aspirin,
oral potassium, other NSAIDs, corticosteroids, or alcohol.
Hypersensitivity (cross-sensitivity may exist with other
NSAIDs, including aspirin).
Active GI bleeding or ulcer disease.
Chewable tablets contain aspartame and should not be
used in patients with phenylketonuria.
headache, GI BLEEDING, constipation, dyspepsia, nausea
and vomiting, EXFOLIATIVE DERMATITIS,
STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME, TOXIC EPIDERMAL
NECROLYSIS, ANAPHYLAXIS.
Decreased pain and inflammation. Reduction
of fever.
Patients who have asthma,
aspirin-induced allergy, and
nasal polyps are at increased
risk for developing
hypersensitivity reactions.
Assess for rhinitis, asthma, and
urticaria.
Decrease in severity of pain.
Improved joint mobility.
Reduction in fever
Caution patient that use of
ibuprofen with 3 or more glasses
of alcohol per day may increase
the risk of GI bleeding.
May cause drowsiness or
dizziness.
Instruct patient to take
medication as directed.