- Information
- AI Chat
HIST 105 - Exam 1 - History of the US with Dr. Damon Bach
(HIST 1301) History of the United States (HIST 105)
Texas A&M University
Recommended for you
Preview text
HIST 105 Notes :
● Long before arrival of Europeans, Indians had occupied and transformed the western hemisphere ● Indians not simply conquered, but had agency; helped build America ● A new world for conquerors and conquered alike ● Africans, Indians and Europeans made a new world together
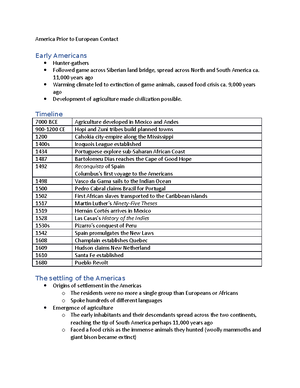
Clovis Peoples ● Nomadic peoples from northeast Asia migrated over “Beringia” 12,000 to 45,000 years ago ● Archaeologists called these “first-peoples”, Paleo-Indians ● Ancient peoples may have arrived by boat ● Agricultural revolutions ● They were skilled hunters/gatherers ● Used weapons knives, spears ● Ate animals, wild plants, berries, and seeds ● More than 300 languages were spoken ● Clovis peoples killed wooly mammoths using special spears ● Lived in small lands of 5-10 families ● Post-ice age many lakes dried into deserts ● After bigger animals started going extinct, hunters hunted more abundant smaller animals - deer, caribou, etc ● Adapted to their environment by becoming a farming society ● Farmed maze, corns, beans, squash, peppers, avocados, pumpkin, etc ● More food = population growth, bigger cities, more industries ● Around 1500 BC farming towns first appeared enabling ppl to live in one place rather than moving w seasons ● pyramids , temples, and palaces in Meso-America (now Mexico; Central America) ● Mayas dominated central America for 600 years made own language and arts, astrology; made calendar ● Mayan civilization was highly developed ● 900 mayan culture collapsed; why is a mystery, but reason was ecological ○ Too many farmers grew too many crops on too many lands
○ Overpopulation caused Mayan wars ● Toltecs took over the Mayan society ● 1200 the Toltecs mysteriously disappeared after invasions ● Inca empire - south America, 15th century ○ Stretched 25 thousand miles across Andes mountains ■ Had fertile farms by irrigation systems ● Mexica (Aztecs) - 13th century took over the entire region ○ Believed that gods sacrificed themselves for mankind ○ Regularly offered people sacrifices to “give back” to gods ○ Cut out beating hearts of victims as sacrifice
North American Civilizations Before 1500 ● Gendered division of labor ● Men were hunters and warriors ● women tended to children, made clothing, jewels, and pottery, and dried animal skins, wove baskets, and cooked food ● families lived together in lodges or teepees ● West (Nevada, Utah, etc) - corn growing societies ● Anasazi and Hohokam built apartment size villages that would protect them from enemies ● Year 500 Hohokam ppl from Mexico migrated to southern/central Arizona and constructed irrigation canals and decorated pottery, turquoise jewelry ● Indigenous ppl drew sustenance from fishing in the northwest ● Ppl of NW designed totem poles ● Hopewell mound-builders are notable for their burial sites and earthworks ● Great plains Indians - nomadic gatherers who killed bison/buffalo on horseback ● Mississippian culture succeeded the Hopewell culture ○ Most successful is Cahokia - largest city north of Mexico at the time ● Iroquois league - in east/NE US, northern NY to PN ○ 5 tribes - mohawks, etc ○ These tribes created a confederacy for strength ○ No private property; community was governed on communal principles ○ Men married into woman’s family; it was easy for women to get a divorce (set men’s things outside); women exercised political power; women did
○ Wanted no ties to the Anglican church ○ Wanted complete separation btw church and state ● General court banished him from new England in 1635 ● Williams and his followers ventured into the wilderness during a blizzard and got away ○ They settled in province Rhode island ● Anne Hutchinson - she, a woman, held group religious meetings in her home ○ She claimed to know which of her neighbors (and ministers) were saved and which were not ○ She tried to “undermine the kingdom of Christ” ○ Settled in Rhode island ○ Moved to new york, and she and her 6 children were massacred by Native Americans
Indians, Indentured Servants, and Slaves in the Colonies
Native People and English Settlers in the Chesapeake ● Jamestown settlers founded village next to native American land ● Early Jamestown leader john Ratcliffe was skinned alive ● John Smith showed native Americans how to plant corn ○ Was captured by N/am ○ Pocahontas convinced N/Am leaders to give up Smith for guns and hatchets ● Colonists increasingly approached on Indian land ● Powhatan War - Indians responded by attacking 30 farms and killed settlers ● Pocahontas was killed by smallpox ● Powhatan confederacy dominated native people of Chesapeake ○ Chief Powhatan 100 villages with 100 people ■ He had 100 wives ● People traded hides and corn to colonists for weapons
Bacon’s Rebellion (1676) ● Nathaniel Bacon and his followers targeted Indians and political elite in VA ● White men with no land worked on the countryside performing crimes ● Falling tobacco prices, rising taxes, and ppl wanted Indian land
● Native Americans killed overseers on a plantation ○ Sparked fighting on the frontier ● Bacon organized a vigilante group to retaliate against the Native Americans ○ Governor William Berkeley was against the rebellion because he was in charge of the fur trade with the Native Americans ■ So caused bacon to target political leaders ● Significance : afterward, plater elite increasingly turned to African slavery as source of labor ● Elite whites grew scared of white indentured servants that get freed and use firearms ○ As a result, more people turned to African slavery as source of labor because they never gain their freedom
Indentured Servants ● White indentured servants from Europe serve masters for 3 to 7 years in return for passage to North America ● Occupied rank between slave and free person ● Did most of the work involving tobacco ● 350,000 came to North America as indentured servants ● Some came against their will, kidnapped ● Convicts tried to avoid being imprisoned by working as an indentured servant ● Had to get permission from master to marry ● Masters could whip them as punishment ● And extend their terms of service ● When term ended, master gave them tools, money, clothes, and sometimes land
Slavery in the 1600s ● Slaves were 20% of the population ● Only 2% were in New England ● Many lived in Chesapeake where agriculture was dominant ● 80% of slaves in Chesapeake were born there ● The Middle Passage ○ A 6-month transatlantic voyage ○ 1 in 6 Africans died
● 16 was average age of Americans in 1790
Women in the Colonies ● Many more women in English colonies than in France and Spain which explains rapid population growth ● Colonists believed women were inferior ● Gendered division of labor ○ Women’s role was to nurture children, tend to husband, and keep house ○ Women could not vote, preach, attend college, make lawsuits, make contracts, or own property ○ Divorces were very difficult to get ○ Men always got custody of children ● Some women did work as shopkeepers, painters, silversmiths, etc ○ Some managed plantations in the south
The Southern Colonies ● Marked differences in clothing, housing, wealth, and status distinguished various people ● “Planters” stood at the top of the socioeconomic hierarchy ● Profitable staple crops : rice, tobacco, indigo ○ Tobacco dominated Virginia ○ Rice planters in south Carolina became wealthiest in British colony ● Indentured servants and slave labor ● Almost 90% of Africans transported to America went to south ○ South Carolina had black majority
The Enlightenment ● Celebrated freedom of thought, rational inquiry, critical thinking, scientific research, political liberty, and individual freedom ● Began to employ reason as a way to understand the workings of nature ○ Telescopes, microscopes, mathematical calculations ● Was triggered by the scientific revolution ● Nicolaus Copernicus discovered that planets revolve around the sun and that the earth was not the center of the universe ○ Although he was a Catholic priest, other priests scorned his theory
● Isaac Newton - theory of gravity ○ Challenged religion ○ Newton said natural laws not god governed these things ● Deism - God made the universe but didn’t intervene in people’s daily lives ○ Believed man was sinful bc of original sin but bc of our imperfect understanding of nature ○ Highest virtue : reason ● John Locke - emphasizes that people have inalienable rights, argues that govt should rest on ppl’s consent
The American Enlightenment ● Benjamin Franklin - started the “American” Enlightenment ○ Had a print shop ○ Founded a library ○ A fire department ○ Helped start U Penn ○ Created American philosophical society ○ Conducted experiments in geology, astronomy,, physics, meteorology ○ Invented Franklin stove, bifocal spectacles, glass harmonica ○ His scientific reason clashed with Christian views
The Great Awakening ● 85% of Americans lived in a colony where the government endorsed and collected taxes to support a single religious denomination ○ Virginia, Maryland, etc - Anglican Church was established ○ New England - Puritan ○ Pennsylvania - Quakers ○ New Jersey / Rhode Island - no official denomination ● Stressed need to be “reborn in religious convictions ● Enlightenment appealed to more educated ppl, but the great awakening involved all colonies ○ It connected ppl ○ Got ppl used to questioning authority ● Jonathan Edwards
■ Argued individuals are endowed with natural rights (life, liberty, and property) and govt was supposed to secure those things ■ People have right to overthrow government and institute a new government
French and Indian War (1764-1763) ● Most significant war fought in America ● Both French and British believed controlling Ohio Valley is key to controlling all of N America ● Washington was sent to tell the french to back off but they refused ● Battle of Great Meadows ○ Washington lost a ⅓ of his forces and french ruled the Ohio Valley ● Albany Plan - met with Iroquois ○ Set a precedent for colonies working together ● General Edward Braddock ● Battle of Monongahela -one of the worst defeats in British history ● Battle of Quebec
Treaty of Paris (1763) ● Concluded the French and Indian War ● France ceded Canada and possessions East of the Mississippi River to Britain ● Spain given control of Louisiana territory, including all land West of the Mississippi ● Spain ceded Florida to Britain
Legacies of French and Indian War ● Doubled Britain’s national debt ● Britain maintained huge army on North American soil ● Britain taxed colonists for upkeep of troops ○ Dispute would lead to revolution
Pontiac’s Rebellion ● Indians renewed frontier warfare in an effort to regain lands ● Royal Proclamation of 1763 ● Settlers were forbidden to venture frontier past the “invisible line”
Tightening Control Over the Colonies ● Sugar Act of 1764
○ Taxed wine, coffee, indigo, and sugar ○ Established a vice-admiralty cords ● Currency Act of 1764 ○ Prevents any of the colonies from printing their own money
Revolution in the Colonies
Grenville’s Colonial Policy ● Stamp Act (1765) ○ Imposed a tax on every printed document ○ Unlike sugar act, stamp act affected all colonies ○ Internal tax (pay tax at point of purchase) ● Quartering Act (1765) ○ Required colonists to provide shelter, supplies, and food for British troops ○ Americans disliked why troops are in cities and not the frontier
Philosophy Behind the Revolt ● Defense of self-government, religious freedom, territorial expansion, and equality of economic opportunity ● Standing army as embodiment of tyranny ● “No taxation without representation” ○ No taxes could be levied without consent of colonists themselves ● Actual vs virtual representation ● Whigs defended parliament and tories wanted monarchy ○ Virtual representation - representation as a whole ○ actual representation - each community is entitled to their own representative
Protest in the Colonies ● Sons of liberty ● “Stamps Act Resolutions” ○ Offered by Patrick Henry ○ Asserted that colonists could not be taxed without consent ● Stamp Act repealed in February 1766 ● Declaratory Act
Townshend Duties
● King George III caused the rebellion ● Called for independence
The Declaration of Independence (1776) ● Follows closely to the content and form of John Locke’s Second treatise ● “Unalienable rights” ● “Life, liberty, and pursuit of happiness” ● “All men are created equal” ● Rhetoric of liberty and equality did not apply to slaves ● Paragraph about slaves was taken out in fear of alienating southern slave owners
The American Revolution
Overview ● America lost most battles, but ultimately won its independence ● Involved European alliances ● Loyalists vs patriots and native American allies ● War unleashed a domestic social and political revolution ● 20% of American population were loyalists
The British and American Militaries ● British had no clear strategy: three failed approaches ○ Britain blocked the ports; tried to destroy continental army in NY; tried to isolate NY from new England; tried to venture into southern colonies ● A war of endurance - America prevailed with the help of the french ● American had to build up an army and navy from the ground up ● Forming a continental army ● Americans had advantage of fighting on their own turf ○ But they had to build army/navy from the ground up ○ No rifle, no uniforms ○ Army was made up of former immigrants, farmers, indentured servants ● Continental army - main army ○ But they had local militias
Native American and Financing the War ● Most natives fought with britain
○ bc they said they would protect their land ● Congress could not levy taxes; states only contributed a small part of their expected share ● War was financed by borrowing from other nations ● States printed currency of their own and caused great inflation
Fighting in Canada ● Smallpox spread throughout the American army ● Americans attack Quebec (1775) ● American general Richard Montgomery had to fight even when his troops had smallpox ● Attacked British soldiers in the middle of a blizzard ○ Montgomery was killed ○ 400 American soldiers were taken prisoner
Fighting in New York ● British strategy was to divide the colonies by capturing New York ● Battle of Long Island and White Plains (1776) ● Thomas Paine: “these are the times that try men’s souls” ● Washington’s hit and run and surprise tactics ● General William Howe ● Washington democratized the army - asked for input and changed accordingly
Battle of Trenton and Princeton ● Battle of Trenton (1776) ○ America won ● Battle of Princeton (1777) ○ America won ● Washington’s strategy of evasion ● Battle of Brandywine Creek (1777) ○ British defeat America ○ British occupies Philadelphia
The American Revolution, 1777-
● General Clinton was determined to capture savannah and charleston and Georgia and South Carolina ○ Objective - To turn American loyalists against patriots and to create slave uprising ○ Successful in capturing savannah and charleston and Georgia and South Carolina ○ Backfired in 3 aspects ■ Brutal native American assault drove many to join patriots ■ Behavior of British and loyalists made some loyalists go over to American side ■ Clinton overestimated how much loyalist forces were in the south cause patriot forces blended into society ● America was defeated in Battle of Charleston (1780) - one of the worst defeats ● Battle of Camden (1780) - despite being outnumbered Cornwallis won the battle ● Civil war between colonists - patriots and loyalists ● Patrick Ferguson and taropen(?) trained loyalists brutally ● Battle of King’s Mountain - loyalists fought 1 hour long battle against patriots ○ Ferguson was the only Britain in this battle ■ Shows signs of “civil war” ○ Ferguson died ○ Family members fought on opposing sides ○ Turning point in the south - many southerners joined patriots after Americans showed they could beat British and loyalists ● Battle of Cowpens (1781) - America won taking 700 British prisoners ● Battle of Guildford Courthouse (1781) - lost to British ● Eventually British only controlled charleston and savannah in the south
● Cornwallis made Yorktown his base ● Battle of Yorktown - Americans combined their forces and won the battle and declared independence ○ Major victory to end revolution with America’s win ● Treaty of Paris (1783) ○ Britain recognized American independence
○ America received all the land from the Atlantic seaboard to Mississippi river ○ Spain regained Florida ○ Pre-war debts paid to merchants ○ Confiscated loyalist properties were returned to original owners
● Newburgh conspiracy ○ Letter circulated among officers arguing for military intervention if congress failed to meet demands ○ Washington stopped/persuaded revolt of officers through celebrating speech ○ Washington prevented a military coup on the exact moment the nation was gaining independence
The Political and Social Revolution
Divided Loyalties and Choosing Sides ● 20% loyalist, 40% patriot, and 40% neutral ● Tore apart families, villages, etc ● Franklin’s son disinherited his son after he chose British side ● Loyalist sentiments ● Loyalists believed British constitution would protect them not the American aristocrats pretending to be revolutionaries ● Lots of subsistence/backcountry farmers were loyalists ● When loyalists were marching through south they set slaves free
The Radicalism of the American Revolution ● Revolution radically altered society and fomented political experimentation ● Monarchial society predicated on deference, patriarchal authority, personal connections and political influence, and fixed rank gave way to a more egalitarian and free society ● Ended slavery in the north
Republican Ideology ● Representative democracy ○ People rule through representatives ○ Representatives make policy on behalf of the people
○ Mostly from northern states ● Ideology of freedom and liberty translated into emancipation for slaves in the North ● Peter Salem and Salem Poor
The Status of Women ● Many women couldn’t even write their own name ● Women served the patriot cause as spies, nurses, cooks, and did sewing and washing ● Some women fought disguised as men ● 1777 Virginia, women battled all day long until enforcements came ● Abigail Adams ○ Told John Adams - “remember the ladies and do not put unlimited power to the husbands” ○ Believed women should have access to education ○ “Women are determined to start a rebellion if they had no voice under law” ○ John Adams said if women had equality the native Americans would ask for equality as well
- What triggered the Enlightenment? a. J
- American that started Enlightenment a. Benjamin Franklin
- What crop was abundant in Jamestown a. Tobacco
- The major distinction between southern and New England colonies a. Different crops (NE - wheat/barley ; VA - tobacco)
- Why did the pilgrim come to the New World a. Religious freedom ; convert the “heathens”
- What are the major battles of the revolution and what are the turning points? a. Lexington and Concord - first two battles b. King’s Mountain - more patriots joined the American cause after the battle c. Battle of Trenton followed by Princeton - George Washington’s sneak attack d. Battle of saratoga - victory that France needed to see to form an alliance with America
e. Battle of Yorktown - French and American forces combine to defeat Cornwallis and end the war 7. Royal Proclamation of 1763 was one of the first “Acts” that made Americans angry. (sugar act, currency act, quartering act, stamp act, taxation without representation, Townsend acts, coercive acts, 8. What are Roger Wiliams and Anne Hutchinson known for? a. Religious dissidence 9. Distinction between the 2 treaty of paris’ a. 1783 - britain recognizes america’s independence, france gives up all their possessions
HIST 105 - Exam 1 - History of the US with Dr. Damon Bach
Course: (HIST 1301) History of the United States (HIST 105)
University: Texas A&M University

- Discover more from: